Page 281 - EJMO-9-3
P. 281
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology WGCNA and LASSO for osteoporosis biomarkers
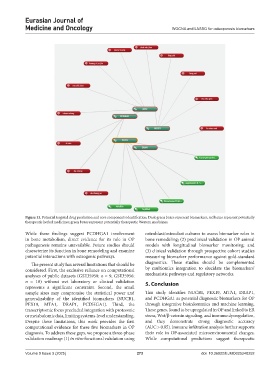
Figure 11. Potential targeted drug prediction and core components identification. Dark green boxes represent biomarkers; red boxes represent potentially
therapeutic herbal medicines; green boxes represent potentially therapeutic Western medicines.
While these findings suggest PCDHGA1 involvement osteoblast/osteoclast cultures to assess biomarker roles in
in bone metabolism, direct evidence for its role in OP bone remodeling; (2) preclinical validation in OP animal
pathogenesis remains unavailable. Future studies should models with longitudinal biomarker monitoring; and
characterize its function in bone remodeling and examine (3) clinical validation through prospective cohort studies
potential interactions with osteogenic pathways. measuring biomarker performance against gold-standard
The present study has several limitations that should be diagnostics. These studies should be complemented
considered. First, the exclusive reliance on computational by multiomics integration to elucidate the biomarkers’
analyses of public datasets (GSE35958: n = 9; GSE35956: mechanistic pathways and regulatory networks.
n = 10) without wet laboratory or clinical validation 5. Conclusion
represents a significant constraint. Second, the small
sample sizes may compromise the statistical power and This study identifies NUCB1, PEX19, MTA1, DRAP1,
generalizability of the identified biomarkers (NUCB1, and PCDHGA1 as potential diagnostic biomarkers for OP
PEX19, MTA1, DRAP1, PCDHGA1). Third, the through integrative bioinformatics and machine learning.
transcriptomic focus precluded integration with proteomic These genes, found to be upregulated in OP and linked to ER
or metabolomic data, limiting systems-level understanding. stress, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and immune dysregulation,
Despite these limitations, this work provides the first and they demonstrate strong diagnostic accuracy
computational evidence for these five biomarkers in OP (AUC > 0.85). Immune infiltration analysis further supports
diagnosis. To address these gaps, we propose a three-phase their role in OP-associated microenvironmental changes.
validation roadmap: (1) in vitro functional validation using While computational predictions suggest therapeutic
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 273 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025240252