Page 276 - EJMO-9-3
P. 276
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology WGCNA and LASSO for osteoporosis biomarkers
A B
C D
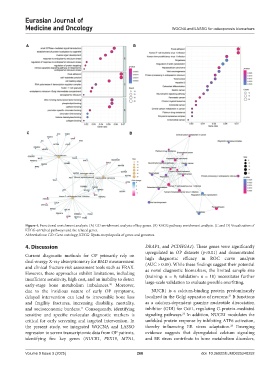
Figure 4. Functional enrichment analysis. (A) GO enrichment analysis of key genes. (B) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. (C and D) Visualization of
KEGG-enriched pathways and the related genes.
Abbreviations: GO: Gene ontology; KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
4. Discussion DRAP1, and PCDHGA1). These genes were significantly
upregulated in OP datasets (p<0.01) and demonstrated
Current diagnostic methods for OP primarily rely on high diagnostic efficacy in ROC curve analysis
dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for BMD measurement (AUC > 0.85). While these findings suggest their potential
and clinical fracture risk assessment tools such as FRAX. as novel diagnostic biomarkers, the limited sample size
However, these approaches exhibit limitations, including
insufficient sensitivity, high cost, and an inability to detect (training: n = 9; validation: n = 10) necessitates further
large-scale validation to evaluate possible overfitting.
early-stage bone metabolism imbalances. Moreover,
20
due to the insidious nature of early OP symptoms, NUCB1 is a calcium-binding protein predominantly
delayed intervention can lead to irreversible bone loss localized in the Golgi apparatus of neurons. It functions
21
and fragility fractures, increasing disability, mortality, as a calcium-dependent guanine nucleotide dissociation
and socioeconomic burdens. Consequently, identifying inhibitor (GDI) for Gαi1, regulating G-protein-mediated
11
sensitive and specific molecular diagnostic markers is signaling pathways. In addition, NUCB1 modulates the
22
critical for early screening and targeted intervention. In unfolded protein response by inhibiting ATF6 activation,
23
the present study, we integrated WGCNA and LASSO thereby influencing ER stress adaptation. Emerging
regression to screen transcriptomic data from OP patients, evidence suggests that dysregulated calcium signaling
identifying five key genes (NUCB1, PEX19, MTA1, and ER stress contribute to bone metabolism disorders,
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 268 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025240252