Page 15 - ESAM-1-2
P. 15
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing AM-CFRP structures for EMWA properties
A B
C D
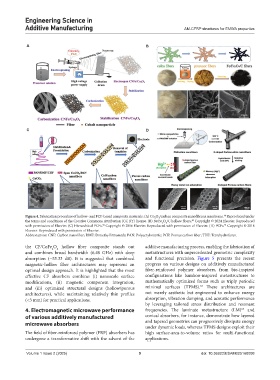
Figure 4. Fabrication procedure of hollow- and PCF-based composite materials: (A) Co O /carbon composite nanofibrous membrane. Reproduced under
48
3
4
the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. (B) Fe/Fe O /C hollow fibers. Copyright © 2024 Elsevier. Reproduced
49
3
4
with permission of Elsevier. (C) Hierarchical PCFs. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (D) PCFs. Copyright © 2018
50
51
Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier.
Abbreviations: CNF: Carbon nanofiber; DMF: Dimethylfirmamide; PAN: Polyacrylonitrile; PCF: Porous carbon fiber; THF: Tetrahydrofuran.
the CF/CoFe O hollow fiber composite stands out additive manufacturing process, enabling the fabrication of
2
4
and combines broad bandwidth (6.48 GHz) with deep metastructures with unprecedented geometric complexity
absorption (−55.33 dB). It is suggested that combined and functional precision. Figure 5 presents the recent
magnetic-hollow fiber architectures may represent an progress on various designs on additively manufactured
optimal design approach. It is highlighted that the most fiber-reinforced polymer absorbers, from bio-inspired
effective CF absorbers combine: (i) nanoscale surface configurations like bamboo-inspired metastructures to
modifications, (ii) magnetic component integration, mathematically optimized forms such as triply periodic
64
and (iii) optimized structural designs (hollow/porous minimal surfaces (TPMS). These architectures are
architectures), while maintaining relatively thin profiles not merely aesthetic but engineered to enhance energy
(<3 mm) for practical applications. absorption, vibration damping, and acoustic performance
by leveraging tailored stress distribution and resonant
4. Electromagnetic microwave performance frequencies. The laminate metastructure (LM) and
65
of various additively manufactured conical absorbers, for instance, demonstrate how layered
microwave absorbers and tapered geometries can progressively dissipate energy
under dynamic loads, whereas TPMS designs exploit their
The field of fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) absorbers has high surface-area-to-volume ratios for multi-functional
undergone a transformative shift with the advent of the applications.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 9 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025160008