Page 18 - ESAM-1-2
P. 18
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing AM-CFRP structures for EMWA properties
A B
C D
E F
G H
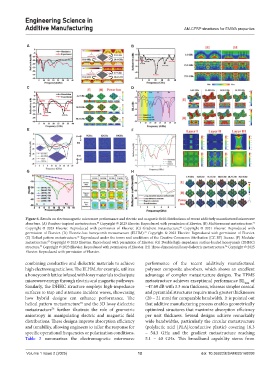
Figure 6. Results on electromagnetic microwave performance and electric and magnetic field distributions of recent additively manufactured microwave
71
absorbers. (A) Bamboo-inspired metastructure. Copyright © 2023 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (B) Multiresonant metastructure.
69
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (C) Gradient metastructure. Copyright © 2021 Elsevier. Reproduced with
66
permission of Elsevier. (D) Electric-loss honeycomb metastructure (ELHM). Copyright © 2023 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier.
22
72
(E) Helical pattern metastructure. Reproduced under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. (F) Modular
metastructure. Copyright © 2023 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (G) Double high-impedance surface-loaded honeycomb (DHHC)
67
76
structure. Copyright © 2023 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (H) Three-dimensional lossy dielectric metastructure. Copyright © 2025
75
Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier.
combining conductive and dielectric materials to achieve performance of the recent additively manufactured
high electromagnetic loss. The ELHM, for example, utilizes polymer composite absorbers, which shows an excellent
a honeycomb lattice infused with lossy materials to dissipate advantage of complex metastructure designs. The TPMS
microwave energy through electric and magnetic pathways. metastructure achieves exceptional performance RL of
min
Similarly, the DHHC structure employs high-impedance −47.60 dB with 3.3 mm thickness, whereas simpler conical
surfaces to trap and attenuate incident waves, showcasing and pyramidal structures require much greater thicknesses
how hybrid designs can enhance performance. The (20 – 21 mm) for comparable bandwidth. It is pointed out
helical pattern metastructure and the 3D lossy dielectric that additive manufacturing process enables geometrically
72
metastructure further illustrate the role of geometric optimized structures that maximize absorption efficiency
76
anisotropy in manipulating electric and magnetic field per unit thickness. Several designs achieve remarkably
distributions. These designs improve absorption efficiency wide bandwidths, particularly the circular metastructure
and tunability, allowing engineers to tailor the response for (polylactic acid [PLA]/conductive plastic) covering 16.3
specific operational frequencies or polarization conditions. – 54.3 GHz and the gradient metastructure reaching
Table 3 summarizes the electromagnetic microwave 5.1 – 40 GHz. This broadband capability stems from
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 12 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025160008