Page 19 - ESAM-1-2
P. 19
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing AM-CFRP structures for EMWA properties
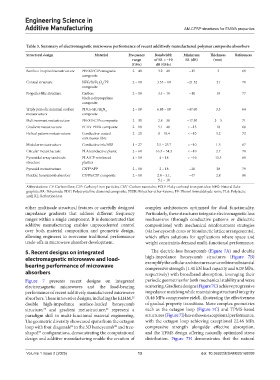
Table 3. Summary of electromagnetic microwave performance of recent additively manufactured polymer composite absorbers
Structural design Material Frequency Bandwidth Minimum Thickness References
range of RL < −10 RL (dB) (mm)
(GHz) dB (GHz)
Bamboo-inspired metastructure PEEK/FCIPs magnetic 2 – 40 3.2 – 40 −15 3 69
composite
Conical structure NFG/Si/Fe O /PF 2 – 18 3.55 – 18 −21.52 21 70
4
3
composite
Propeller-like structure Carbon 2 – 18 3.4 – 10 −10 10 77
black-polypropylene
composite
Triply periodic minimal surface PDCs-SiC/Si N 4 2 – 18 6.88 – 18 −47.60 3.3 64
3
metastructure composite
Multiresonant metastructure PEEK/FCIPs composite 2 – 30 2.8 – 30 −17.50 3 – 5 71
Gradient metastructure FCIPs-PEEK composite 2 – 18 5.1 – 40 < −15 10 66
Helical pattern metastructure Conductive-coated 2 – 20 8 – 18.4 < −10 3.2 72
continuous fibre
Modular metastructure Conductive ink/ABS 1 – 27 3.5 – 25.7 < −10 1.5 67
Circular metastructure PLA/conductive plastic 2 – 60 16.3 – 54.3 < −10 2.7 78
Pyramidal array sandwich PLA/CF-reinforced 4 – 18 4 – 18 ≈ −10 13.5 68
structure plastics
Pyramid metastructure CNT APP 2 – 18 2 – 18 −30 20 79
@
Flexible honeycomb absorber CF/PA/CIP composite 2 – 18 2.8 – 3.1, −47 2.8 80
5.1 – 18
Abbreviations: CF: Carbon fiber; CIP: Carbonyl iron particles; CNT: Carbon nanotube; FCIP: Flaky carbonyl iron particles; NFG: Natural flake
graphite; PA: Polyamide; PDC: Polycrystalline diamond composite; PEEK: Polyether-ether-ketone; PF: Phenol formaldehyde resin; PLA: Polylactic
acid; RL: Reflection loss.
either multiscale structural features or carefully designed complex architectures optimized for dual functionality.
impedance gradients that address different frequency Particularly, these structures integrate electromagnetic loss
ranges within a single component. It is demonstrated that mechanisms (through conductive patterns or dielectric
additive manufacturing enables unprecedented control compositions) with mechanical reinforcement strategies
over both material composition and geometric design, (via honeycomb cores or biomimetic lattice arrangements),
allowing engineers to overcome traditional performance which offers solutions for applications where space and
trade-offs in microwave absorber development. weight constraints demand multi-functional performance.
5. Recent designs on integrated The electric-loss honeycomb (Figure 7A) and double
electromagnetic microwave and load- high-impedance honeycomb structures (Figure 7B)
exemplify the cellular architectures can combine substantial
bearing performance of microwave compressive strength (1.41 kN load capacity and 6.09 MPa,
absorbers respectively) with broadband absorption, leveraging their
Figure 7 presents recent designs on integrated periodic geometries for both mechanical stability and wave
electromagnetic microwaves and the load-bearing scattering. Gradient designs (Figure 7C) achieve progressive
performance of recent additively manufactured microwave impedance matching while maintaining structural integrity
absorbers. These innovative designs, including the ELHM, (8.46 MPa compressive yield), illustrating the effectiveness
22
double high-impedance surface-loaded honeycomb of gradual property transitions. More complex geometries
66
structure, and gradient metastructure, represent a such as the octagon loop (Figure 7C) and TPMS-based
75
paradigm shift in multi-functional material engineering. structures (Figure 7I) have shown exceptional performance,
The geometric diversity showcased spans from the octagon with the octagon loop achieving exceptional 22.46 MPa
loop with four diagonals to the 3D honeycomb and tree- compressive strength alongside effective absorption,
82
81
shaped configurations, demonstrating the computational and the TPMS design offering naturally optimized stress
83
design and additive manufacturing enable the creation of distribution. Figure 7H demonstrates that the natural
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 13 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025160008