Page 21 - ESAM-1-2
P. 21
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing AM-CFRP structures for EMWA properties
A B
C D
E F
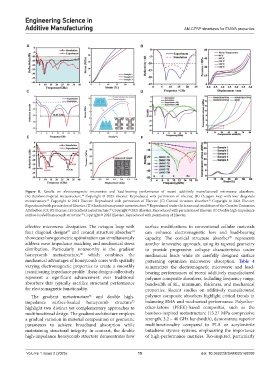
Figure 8. Results on electromagnetic microwave and load-bearing performance of recent additively manufactured microwave absorbers.
69
(A) Bamboo-inspired metastructure. Copyright © 2023 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (B) Octagon loop with four diagonals
81
metastructure. Copyright © 2021 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (C) Conical structure absorber. Copyright © 2024 Elsevier.
70
86
Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (D) Gradient honeycomb metastructure. Reproduced under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons
Attribution (CC BY) license. (E) Gradient metastructure. Copyright © 2021 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier. (F) Double high-impedance
66
surface-loaded honeycomb structure. Copyright © 2023 Elsevier. Reproduced with permission of Elsevier.
75
effective microwave dissipation. The octagon loop with surface modifications to conventional cellular materials
four diagonal designs and conical structure absorber can enhance electromagnetic loss and load-bearing
70
81
showcases how geometric optimization can simultaneously capacity. The conical structure absorber represents
70
address wave impedance matching and mechanical stress another innovative approach, using its tapered geometry
distribution. Particularly noteworthy is the gradient to provide progressive collapse characteristics under
honeycomb metastructure, which combines the mechanical loads while its carefully designed surface
86
mechanical advantages of honeycomb cores with spatially patterning optimizes microwave absorption. Table 4
varying electromagnetic properties to create a smoothly summarizes the electromagnetic microwave and load-
transitioning impedance profile. These designs collectively bearing performances of recent additively manufactured
represent a significant advancement over traditional polymer composite absorbers, including frequency range,
absorbers that typically sacrifice structural performance bandwidth of RL, minimum, thickness, and mechanical
for electromagnetic functionality. properties. Recent studies on additively manufactured
The gradient metastructure and double high- polymer composite absorbers highlight critical trends in
66
impedance surface-loaded honeycomb structure balancing EMA and mechanical performance. Polyether-
75
highlight two distinct yet complementary approaches to ether-ketone (PEEK)-based composites, such as the
multifunctional design. The gradient architecture employs bamboo-inspired metastructure (13.27 MPa compressive
a gradual variation in material composition or geometric strength, 3.2 – 40 GHz bandwidth), demonstrate superior
parameters to achieve broadband absorption while multifunctionality compared to PLA or acrylonitrile
maintaining structural integrity. In contrast, the double butadiene styrene systems, emphasizing the importance
high-impedance honeycomb structure demonstrates how of high-performance matrices. Bio-inspired, particularly
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 15 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025160008