Page 137 - GHES-2-1
P. 137
Global Health Econ Sustain Elderly people with dementia
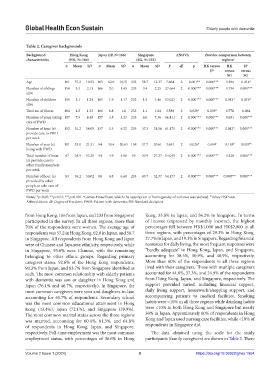
Table 2. Caregiver backgrounds
Background Hong Kong Japan (JP, N=166) Singapore ANOVA Post hoc comparison between
characteristics (HK, N=164) (SG, N=233) regions a
n Mean SD n Mean SD n Mean SD F df p HK versus HK JP
JP versus versus
SG SG
Age 161 57.2 10.52 165 62.0 10.51 233 58.7 12.37 7.664 2 0.001** 0.000*** 0.384 0.014*
Number of siblings 158 3.3 2.11 166 2.0 1.45 233 3.4 2.25 27.664 2 0.000*** 0.000*** 0.734 0.000***
alive
Number of children 159 1.1 1.24 165 1.9 1.17 233 1.5 1.46 13.027 2 0.000*** 0.000*** 0.013* 0.019*
alive
Total no. of illness 164 1.2 1.32 166 0.8 1.0 233 1.1 1.04 3.588 2 0.028* 0.039* 0.778 0.064
Number of years taking 157 7.9 8.45 157 3.5 3.23 233 6.0 7.36 16.411 2 0.000*** 0.000*** 0.051 0.000***
care of PWD
Number of hour (s) 152 51.2 54.09 137 5.3 6.32 233 37.3 31.56 61.175 2 0.000*** 0.000*** 0.012* 0.000***
provide care to PWD
per week
Number of year (s) 101 33.0 21.31 84 30.4 20.65 158 37.7 20.61 3.683 2 0.026* 0.684 b 0.185 b 0.029* b
living with PWD
Total number of hour 67 38.9 53.26 54 4.9 4.06 59 30.9 27.27 14.045 2 0.000*** 0.000*** 0.528 0.000***
(s) provide care to
other family members
per week
Number of hour (s) 83 76.2 50.02 88 4.8 6.60 233 49.7 52.37 54.177 2 0.000*** 0.000*** 0.000*** 0.000***
provided by other
people to take care of
PWD per week
Notes: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. Games-Howell test, which the assumption of homogeneity of variance was violated. Tukey HSD test.
b
a
Abbreviations: df: Degree of freedom; PWD: Patient with dementia; SD: Standard deviation.
from Hong Kong, 166 from Japan, and 233 from Singapore) Kong, 35.5% in Japan, and 56.2% in Singapore. In terms
participated in the survey. In all three regions, more than of income (expressed by monthly income), the highest
70% of the respondents were women. The average age of percentages fell between HK$1,000 and HK$2,000 in all
respondents was 57.2 in Hong Kong, 62.0 in Japan, and 58.7 three regions, with percentages of 29.3% in Hong Kong,
in Singapore. All respondents from Hong Kong and Japan 27.7% in Japan, and 19.3% in Singapore. Regarding financial
were of Chinese and Japanese ethnicity, respectively, while resources for daily living, the most frequent responses were
in Singapore, 93.6% were Chinese, with the remaining “hardly adequate” in Hong Kong, Japan, and Singapore,
belonging to other ethnic groups. Regarding primary accounting for 38.5%, 50.9%, and 48.9%, respectively.
caregiver status, 92.6% of the Hong Kong respondents, More than 60% of the respondents in all three regions
90.3% from Japan, and 83.7% from Singapore identified as lived with their caregivers. Those with multiple caregivers
such. The most common relationship with elderly patients accounted for 44.8%, 37.3%, and 24.9% of the respondents
with dementia was son or daughter in Hong Kong and from Hong Kong, Japan, and Singapore, respectively. The
Japan (76.1% and 46.7%, respectively). In Singapore, the support provided varied, including financial support,
most common caregivers were sons and daughters-in-law, daily living support, housework/shopping support, and
accounting for 65.7% of respondents. Secondary school accompanying patients to medical facilities. Smoking
was the most common educational attainment in Hong habits were <10% in all three regions while drinking habits
Kong (43.4%), Japan (72.1%), and Singapore (39.9%). were <10% in both Hong Kong and Singapore but nearly
The most common marital status across the three regions 30% in Japan. Approximately 60% of respondents in Hong
was married, accounting for 60.4%, 81.3%, and 64.8% Kong and Japan used nursing care facilities, while <10% of
of respondents in Hong Kong, Japan, and Singapore, respondents in Singapore did.
respectively. Full-time employment was the most common The data obtained using the scale for the study
employment status, with percentages of 36.6% in Hong participants (family caregivers) are shown in Table 3. There
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1954