Page 31 - GHES-3-1
P. 31
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Peace and quality health is entrepreneurship
snips or scrapings. If lesions, pus, or open wounds are professionally (Börjesson et al., 2017; Chiari & Gojanovic,
present, pus or wound swabs should be collected (Ashoobi 2023; Yung et al., 2022). Microbiological diagnosis through
et al., 2023; Phan et al., 2023). In cases of respiratory tract culture and sensitivity testing determines the most effective
infections, such as pharyngitis, a throat swab is the most or sensitive antimicrobial agents that can destroy or inhibit
reliable sample (Vorvick, 2021) (Figure 3). Proper sample pathogens (Go et al., 2022; Kamde & Anjankar, 2022;
collection is crucial, as incorrect techniques can lead to Papavarnavas et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023). This process
inaccurate results. simplifies the interpretation of results for physicians or
Wound swabs are collected from skin infections consultants, enabling them to provide targeted treatment
containing pus or exudates and from open wounds using that facilitates athletes’ recovery and return to play (Go
a sterile swab stick (Ashoobi et al., 2023; Cravez et al., et al., 2022; Kristóf & Pongrácz, 2016; Turner et al., 2019).
2020; Phan et al., 2023). Samples such as blood, pus, Microbiology plays a critical role in most medical
wound swabs, sputum, urine, stool, cerebrospinal fluid, laboratory diagnoses, confirming infections and diseases
and high vaginal swabs can be stained directly. Culturing for patient treatment and disease prevention. For instance,
the pathogen represents another effective method for when blood is used to investigate which infectious agent
pathogen identification (Ashurst & Edgerley-Gibb, 2023; is responsible for an outbreak, it highlights the linkage
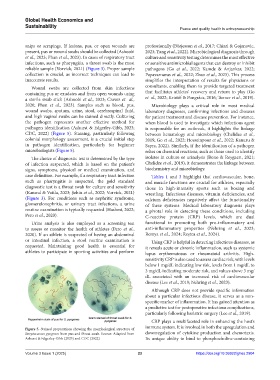
CDC, 2022) (Figure 5). Staining, particularly following between hematology and microbiology (Chelidze et al.,
colonial morphology assessment, is a crucial initial step 2019; Go et al., 2022; Hosseinpour et al., 2022; Kanuru &
in pathogen identification, particularly for beginner Sapra, 2022). Similarly, if the identification of a pathogen
microbiologists (Figure 5). relies on chemical reactions, such as those used to identify
The choice of diagnostic test is determined by the type isolates in culture or urinalysis (Bono & Reygaert, 2021;
of infection suspected, which is based on the patient’s Chelidze et al., 2019), it demonstrates the linkage between
signs, symptoms, physical or medical examination, and biochemistry and microbiology.
case definition. For example, if a respiratory tract infection Tables 1 and 3 highlight that cardiovascular, bone,
such as pharyngitis is suspected, the gold standard and muscle functions are crucial for athletes, especially
diagnostic test is a throat swab for culture and sensitivity those in high-intensity sports such as boxing and
(Kanwal & Vaitla, 2023; Şahin et al., 2022; Vorvick, 2021) wrestling. Infectious diseases, vitamin deficiencies, and
(Figure 3). For conditions such as nephritic syndrome, calcium deficiencies negatively affect the functionality
glomerulonephritis, or urinary tract infections, a urine of these systems. Medical laboratory diagnosis plays
routine examination is typically requested (Hashmi, 2022; a pivotal role in detecting these conditions, including
Pero et al., 2020). C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, which are dual
Urine analysis is also employed as a screening test functional in promoting both pro-inflammatory and
to assess or monitor the health of athletes (Pero et al., anti-inflammatory properties (Nehring et al., 2023;
2020). If an athlete is suspected of having an abdominal Remya et al., 2024; Reștea et al., 2024).
or intestinal infection, a stool routine examination is Using CRP is helpful in detecting infectious diseases, as
requested. Maintaining good health is essential for it reveals acute or chronic inflammation, such as systemic
athletes to participate in sporting activities and perform lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. High-
sensitivity CRP is also used to assess cardiac risk, with levels
below 1 mg/dL indicating low risk, levels from 1 mg/dL to
3 mg/dL indicating moderate risk, and values above 3 mg/
dL associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular
disease (Lee et al., 2019; Nehring et al., 2023).
Although CRP does not provide specific information
about a particular infectious disease, it serves as a non-
specific marker of inflammation. It has gained attention as
a predictive test for postoperative infectious complications,
particularly following bariatric surgery (Lee et al., 2019).
CRP plays a multifaceted role in enhancing the host’s
immune system. It is involved in both the upregulation and
Figure 5. Stained preparations showing the morphological structure of
Streptococcus pyogenes from pus and throat swab. Source: Adapted from downregulation of cytokine production and chemotaxis.
Ashurst & Edgerley-Gibb (2023) and CDC (2022) Its unique ability to bind to phosphocholine-containing
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 23 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.2904