Page 66 - GPD-2-1
P. 66
Gene & Protein in Disease Pyroptosis-related LncRNAs in pediatric AML
A B
C D E
F G
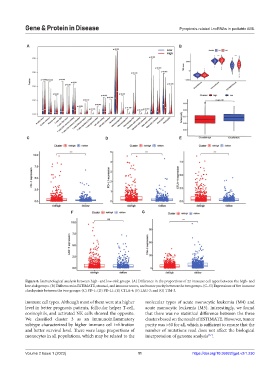
Figure 8. Immunological analysis between high- and low-risk groups. (A) Difference in the proportions of 22 immune cell types between the high- and
low-risk groups. (B) Differences in ESTIMATE, stromal, and immune scores, and tumor purity between the two groups. (C–G) Expressions of five immune
checkpoints between the two groups: (C) PD-1; (D) PD-L1; (E) CTLA-4; (F) LAG-3; and (G) TIM-3.
immune cell types. Although most of them were at a higher molecular types of acute monocytic leukemia (M4) and
level in better prognosis patients, follicular helper T-cell, acute monocytic leukemia (M5). Interestingly, we found
eosinophils, and activated NK cells showed the opposite. that there was no statistical difference between the three
We classified cluster 3 as an immunoinflammatory clusters based on the result of ESTIMATE. However, tumor
subtype characterized by higher immune cell infiltration purity was >60 for all, which is sufficient to ensure that the
and better survival level. There were large proportions of number of mutations read does not affect the biological
monocytes in all populations, which may be related to the interpretation of genome analysis .
[27]
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 11 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v2i1.230