Page 46 - GPD-2-3
P. 46
Gene & Protein in Disease Effect of phytochemicals in diabetes
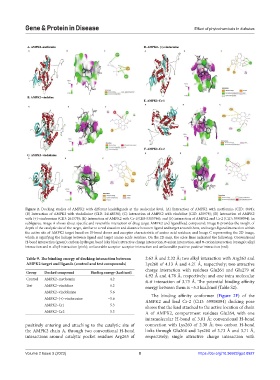
Figure 2. Docking studies of AMPK2 with different leads/ligands at the molecular level. (A) Interaction of AMPK2 with metformin (CID: 4091);
(B) Interaction of AMPK2 with vindolinine (CID: 24148538); (C) Interaction of AMPK2 with vindoline (CID: 425978); (D) Interaction of AMPK2
with (+)-vindorosine (CID: 261578); (E) Interaction of AMPK2 with Cr-1(CID-5315746); and (F) interaction of AMPK2 and Cr-2 (CID: 59908094). In
subfigures, Image A shows about specific and reversible interaction of drug target AMPK2 and ligand/lead compound; Image B provides the insight of
depth of the catalytic site of the target, similar to a real situation and distance between ligand and target around them, and target-ligand interaction within
the active site of AMPK2 target based on H-bond donor and acceptor characteristic of amino acid residues; and Image C representing the 2D image,
which is signifying the linkage between ligand and target amino acids residues. On the 2D map, the color lines indicated the following: Conventional
H-bond interaction (green); carbon-hydrogen bond (sky blue); attractive charge interaction, π-anion interaction, and π-cation interaction (orange); alkyl
interaction and π-alkyl interaction (pink); unfavorable acceptor-acceptor interaction and unfavorable positive-positive interaction (red).
Table 9. The binding energy of docking interaction between 2.63 Å and 2.32 Å; two alkyl interaction with Arg263 and
AMPK2 target and ligands (control and test compounds) Lys260 of 4.13 Å and 4.21 Å, respectively; two attractive
charge interaction with residues Glu264 and Glu279 of
Group Docked compound Binding energy (kcal/mol) 4.92 Å and 4.78 Å, respectively; and one intra molecular
Control AMPK2–metformin −4.2 π-σ interaction of 3.73 Å. The potential binding affinity
Test AMPK2–vindoline −6.2 energy between them is −5.3 kcal/mol (Table S2).
AMPK2–vindolinine −5.6
The binding affinity conformer (Figure 2F) of the
AMPK2–(+)-vindorosine −5.6 AMPK2 and lead Cr-2 (CID: 59908094) docking pose
AMPK2–Cr1 −5.3 shows that the lead attached to the active location of chain
AMPK2–Cr2 −5.3 A of AMPK2, compartment residues Glu264, with one
intramolecular H-bond of 3.01 Å; conventional H-bond
positively entering and attaching to the catalytic site of connection with Lys260 of 2.30 Å; two carbon H-bond
the AMPK2 chain A, through two conventional H-bond links through Glu264 and Lys260 of 3.73 Å and 3.71 Å,
interactions around catalytic pocket residues Arg263 of respectively; single attractive charge interaction with
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.0927