Page 49 - GPD-2-3
P. 49
Gene & Protein in Disease Effect of phytochemicals in diabetes
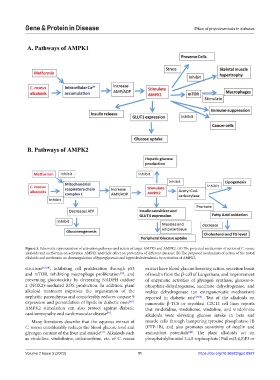
Figure 3. Schematic representation of activation pathways and action of target AMPK1 and AMPK2. (A) The projected mechanism of action of C. roseus
alkaloids and metformin on activation AMPK1 and their effect on prevention of different diseases; (B) The proposed mechanism of action of the tested
alkaloids and metformin on downregulation of hyperglycemia and hypercholesterolemia by activation of AMPK2.
structure [63,64] , inhibiting cell proliferation through p53 extract have blood glucose lowering action, secretion boost
and mTOR, inhibiting macrophage proliferation , and of insulin from the β-cell of Langerhans, and improvement
[16]
preventing glucotoxicity by decreasing NADPH oxidase of enzymatic activities of glycogen synthase, glucose-6-
2 (NOX2)-mediated ROS production. In addition, plant phosphate-dehydrogenase, succinate dehydrogenase, and
alkaloid treatment improves the organization of the malate dehydrogenase (an extrapancreatic mechanism)
nephritic parenchyma and considerably reduces caspase 9 reported in diabetic rats [28,66] . Test of the alkaloids on
expression and peroxidation of lipids in diabetic ones . pancreatic β-TC6 or myoblast C2C12 cell lines reports
[65]
AMPK2 stimulation can also protect against diabetic that vindolidine, vindolicine, vindoline, and vindolinine
cardiomyopathy and cardiovascular disease . alkaloids were elevating glucose intake in beta and
[61]
Many literatures describe that the aqueous extract of muscle cells through hampering tyrosine phosphatase-1B
C. roseus considerably reduces the blood glucose level and (PTP-1B), and also promotes sensitivity of insulin and
glycogen content of the liver and muscle . Alkaloids such antioxidant potentials . The plant alkaloids act on
[44]
[31]
as vindoline, vindolinine, catharanthine, etc. of C. roseus phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate [Ptdlns(3,4,5)P3 or
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 11 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.0927