Page 62 - GPD-2-4
P. 62
Gene & Protein in Disease K fragment for resistance gene hunting
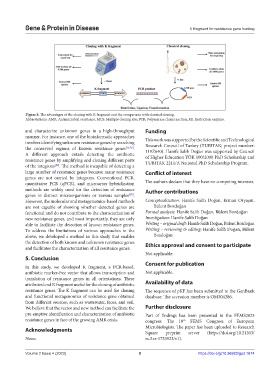
Figure 8. The advantages of the cloning with K fragment and the comparison with classical cloning.
Abbreviations: AMR: Antimicrobial resistance; MCS: Multiple cloning site; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; RE: Restriction enzyme.
and characterize unknown genes in a high-throughput Funding
manner. For instance, one of the bioinformatic approaches This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological
involves identifying unknown resistance genes by searching
the conserved regions of known resistance genes [25,26] . Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK; project number:
119Z640). Hanife Salih Doğan was supported by Council
A different approach entails detecting the antibiotic of Higher Education YÖK 100/2000 PhD Scholarship and
resistance genes by amplifying and cloning different parts TUBITAK 2211/A National PhD Scholarship Program.
of the integrons . The method is incapable of detecting a
[27]
large number of resistance genes because many resistance Conflict of interest
genes are not carried by integrons. Conventional PCR,
quantitative PCR (qPCR), and microarray hybridization The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
methods are widely used for the detection of resistance Author contributions
[28]
genes in distinct microorganisms or various samples .
However, the molecular and metagenomics-based methods Conceptualization: Hanife Salih Doğan, Erman Oryaşın,
are not capable of showing whether detected genes are Bülent Bozdoğan
functional and do not contribute to the characterization of Formal analysis: Hanife Salih Doğan, Bülent Bozdoğan
new resistance genes, and most importantly, they are only Investigation: Hanife Salih Doğan
able to facilitate the detection of known resistance genes. Writing – original draft: Hanife Salih Doğan, Bülent Bozdoğan
To address the limitations of various approaches in the Writing – reviewing & editing: Hanife Salih Doğan, Bülent
above, we developed a method in this study that enables Bozdoğan
the detection of both known and unknown resistance genes Ethics approval and consent to participate
and facilitates the characterization of all resistance genes.
Not applicable.
5. Conclusion
Consent for publication
In this study, we developed K fragment, a PCR-based,
antibiotic marker-free vector that allows transcription and Not applicable.
translation of resistance genes in all orientations. These
attributes lend K fragment useful for the cloning of antibiotic Availability of data
resistance genes. The K fragment can be used for cloning The sequence of pKF has been submitted to the GenBank
and functional metagenomics of resistance gene obtained database. The accession number is OM304286.
from different sources, such as wastewater, feces, and soil.
We believe that the vector and new method can facilitate the Further disclosure
pre-emptive identification and characterization of antibiotic Part of findings has been presented in the FEMS2023
resistance genes in face of the growing AMR crisis. congress: The 10 FEMS Congress of European
th
Acknowledgments Microbiologists. The paper has been uploaded to Research
Square preprint server (https://doi.org/10.21203/
None. rs.3.rs-1723923/v1).
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.1674