Page 49 - GPD-3-1
P. 49
Gene & Protein in Disease Prognostic potential of LMNB2 in LPS
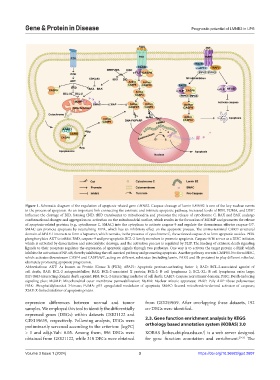
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the regulation of apoptosis-related gene LMNB2. Caspase cleavage of lamin LMNB2 is one of the key nuclear events
in the process of apoptosis. As an important link connecting the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathway, increased levels of BIM, PUMA, and DISC
influence the cleavage of BID, forming tBID. tBID translocates to mitochondria and promotes the release of cytochrome C. BAX and BAK undergo
conformational changes and aggregation on activation on the mitochondrial surface, which results in the formation of MOMP and promotes the release
of apoptosis-related proteins (e.g., cytochrome C, SMAC) into the cytoplasm to activate caspase-9 and regulate the downstream effector caspase-3/7.
SMAC can promote apoptosis by neutralizing XIPA, which has an inhibitory effect on the apoptotic process. The amino-terminal CARD structural
domain of APAF-1 interacts to form a heptamer, which recruits, in the presence of cytochrome C, the activated caspase-9 to form apoptotic vesicles. PI3K
phosphorylates AKT to inhibit BAD, caspase-9 and pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family members to promote apoptosis. Caspase-8/10 serves as a DISC initiator,
which is activated by dimerization and autocatalytic cleavage, and the activation process is regulated by FLIP. The binding of extrinsic death signaling
ligands to their receptors regulates the expression of apoptotic signals through two pathways. One way is to activate the target protein c-FLIP, which
inhibits the activation of NF-κB, thereby inhibiting the cell survival pathway and promoting apoptosis. Another pathway recruits CASP8/10 to form DISC,
which activates downstream CASP4 and CASP3/6/7, acting on different substrates (including lamin, PARP, and Rb proteins) to play different roles but
ultimately promoting apoptotic progression.
Abbreviations: AKT: As known as Protein Kinase B (PKB); APAF1: Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1; BAD: BCL-2-associated agonist of
cell death; BAK: BCL-2 antagonist/killer; BAX: BCL-2-associated X protein; BCL-2: B cell lymphoma 2; BCL-XL: B cell lymphoma extra large;
BID: BH3-interacting domain death agonist; BIM: BCL-2-interacting mediator of cell death; CARD: Caspase recruitment domain; DISC: Death-inducing
signaling plex; MOMP: Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization; NuMA: Nuclear mitotic apparatus; PARP: Poly ADP-ribose polymerase;
PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PUMA: p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis; SMAC: Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases;
XIAP: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.
expression differences between normal and tumor from GSE259659. After overlapping these datasets, 192
samples. We employed this tool to identify the differentially co-DEGs were identified.
expressed genes (DEGs) within datasets GSE21122 and
GES159659, respectively. Following analysis, DEGs were 2.3. Gene function enrichment analysis by KEGG
preliminarily screened according to the criterion: |logFC| orthology based annotation system (KOBAS) 3.0
> 1 and adj.p.Val< 0.05. Among them, 896 DEGs were KOBAS [kobas.cbi.pku.edu.cn/] is a web server designed
obtained from GSE21122, while 318 DEGs were obtained for gene function annotation and enrichment. 29-31 The
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.2607