Page 12 - GTM-1-1
P. 12
Global Translational Medicine ZnO NPs induce apoptosis in MG63 cells
A B
C
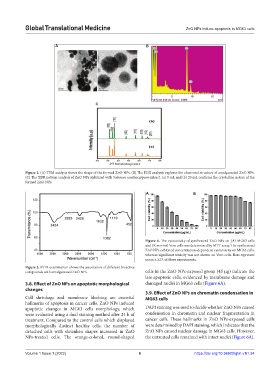
Figure 2. (A) TEM analysis shows the shape of the formed ZnO NPs. (B) The EDX analysis explores the elemental structure of amalgamated ZnO NPs.
(C) The XDR pattern analysis of ZnO NPs stabilized with Solanum xanthocarpum extract: (a) 5 mL and (b) 20 mL confirms the crystalline nature of the
formed ZnO NPs.
A B
Figure 4. The cytotoxicity of synthesized ZnO NPs on (A) MG63 cells
and (B) normal Vero cells was determined by MTT assay. The synthesized
ZnO NPs exhibited concentration-dependent cytotoxicity on MG63 cells,
whereas significant toxicity was not shown on Vero cells. Bars represent
mean ± S.D. of three experiments.
Figure 3. FTIR examination shows the association of different bioactive
compounds with amalgamated ZnO NPs. cells in the ZnO NPs-exposed group (45 µg) indicate the
late apoptotic cells, evidenced by membrane damage and
3.8. Effect of ZnO NPs on apoptotic morphological damaged nuclei in MG63 cells (Figure 6A).
changes
3.9. Effect of ZnO NPs on chromatin condensation in
Cell shrinkage and membrane bleebing are essential MG63 cells
hallmarks of apoptosis in cancer cells. ZnO NPs induced
apoptotic changes in MG63 cells morphology, which DAPI staining was used to decide whether ZnO NPs caused
were evaluated using a dual staining method after 24 h of condensation in chromatin and nuclear fragmentation in
treatment. Compared to the control cells which displayed cancer cells. These hallmarks in ZnO NPs-exposed cells
morphologically distinct healthy cells, the number of were determined by DAPI staining, which indicates that the
detached cells with shrunken shapes increased in ZnO ZnO NPs caused nuclear damage in MG63 cells. However,
NPs-treated cells. The orange-colored, round-shaped the untreated cells remained with intact nuclei (Figure 6A).
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i1.34