Page 15 - GTM-1-1
P. 15
Global Translational Medicine ZnO NPs induce apoptosis in MG63 cells
A B
C D
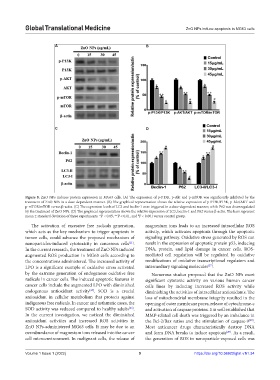
Figure 8. ZnO NPs induces protein expression in MG63 cells. (A) The expression of p-P13K, p-Akt and p-mTOR was significantly inhibited by the
treatment of ZnO NPs in a dose-dependent manner. (B) The graphical representation shows the relative expression of p-P13K/P13K, p-Akt/AKT and
p-mTOR/mTOR versus β-actin. (C) The expression levels of LC3 and beclin-1 were triggered in a dose-dependent manner, while P62 was downregulated
by the treatment of ZnO NPs. (D) The graphical representation shows the relative expression of LC3, beclin-1 and P62 versus β-actin. The bars represent
#
mean ± standard deviation of three experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and P < 0.001 versus control group.
The activation of excessive free radicals generation, magnesium ions leads to an increased intracellular ROS
which acts as the key mechanism to trigger apoptosis in activity, which activates apoptosis through the apoptotic
tumor cells, could advance the proposed mechanism of signaling pathway. Oxidative stress generated by ROS can
nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity in cancerous cells . result in the expression of apoptotic protein p53, inducing
[21]
In the current research, the treatment of ZnO NPs induced DNA, protein, and lipid damage in cancer cells. ROS-
augmented ROS production in MG63 cells according to mediated cell regulation will be regulated by oxidative
the concentrations administered. The increased activity of modifications of oxidative transcriptional regulators and
[27]
LPO is a significant example of oxidative stress activated intermediary signaling molecules .
by the extreme generation of endogenous oxidative free Numerous studies proposed that the ZnO NPs exert
radicals in cancer cells. The induced apoptotic features in significant cytotoxic activity on various human cancer
cancer cells include the augmented LPO with diminished cells lines by inducing increased ROS activity while
endogenous antioxidant activity . SOD is a crucial diminishing the activities of intracellular antioxidants. The
[25]
antioxidant in cellular metabolism that protects against loss of mitochondrial membrane integrity resulted in the
indigenous free radicals. In cancer and asthmatic cases, the opening of outer membrane pores, release of cytochrome-c
SOD activity was reduced compared to healthy adults . and activation of caspase proteins. It is well established that
[26]
In the current investigation, we noticed the diminished MMP-related cell death was triggered by an imbalance in
antioxidant activities and increased ROS activities in the Bcl-2/Bax ratios and the stimulation of caspase-9 .
[28]
ZnO NPs-administered MG63 cells. It may be due to an Most anticancer drugs characteristically destroy DNA
overabundance of magnesium ions released into the cancer and form DNA breaks to induce apoptosis . As a result,
[29]
cell microenvironment. In malignant cells, the release of the generation of ROS in nanoparticle-exposed cells was
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i1.34