Page 31 - GTM-1-1
P. 31
Global Translational Medicine Inflammatory gene-environment interactions in COPD
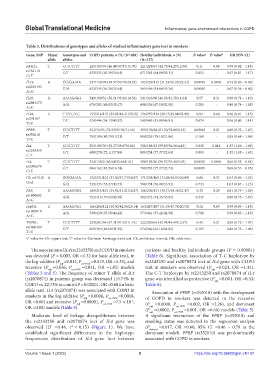
Table 3. Distributions of genotypes and alleles of studied inflammatory gene loci in smokers
Gene, SNP Minor Genotypes and COPD patients, n (%) (N=484) Healthy individuals, n (%) P‑value a P‑value b OR (95% CI)
allele alleles (N=517)
FASLG, T CC/CT/TT 225/183/76 (46.49/37.81/15.70) 221/229/67 (42.75/44.29/12.96) 0.11 0.88 0.99 (0.82 – 1.18)
rs763110 C/T 633/335 (65.39/34.61) 671/363 (64.89/35.11) 0.852 - 0.97 (0.81 – 1.17)
C>T
IL19, A GG/GA/AA 237/149/98 (48.97/30.79/20.25) 163/239/115 (31.53/46.23/22.24) 0.00001 0.0003 0.72 (0.60 – 0.86)
rs2243193 G/A 623/345 (64.36/35.64) 565/469 (54.64/45.36) 0.00001 - 0.67 (0.56 – 0.80)
A>G
IL20, G AA/AG/GG 243/190/51 (50.21/39.26/10.54) 241/216/60 (46.62/41.78/11.61) 0.57 0.31 0.90 (0.74 – 1.10)
rs2981573 A/G 676/292 (69.83/30.17) 698/336 (67.50/32.50) 0.283 - 0.88 (0.74 – 1.08)
A>G
IL24, C TT/TC/CC 155/214/115 (32.02/44.21/23.76) 156/237/124 (30.17/45.84/23.98) 0.82 0.66 0.96 (0.81 – 1.15)
rs291107 T/C 524/444 (54.13/45.87) 549/485 (53.09/46.91) 0.674 - 0.96 (0.80 – 1.14)
T>C
PPBP, T CC/CT/TT 353/76/55 (72.93/15.70/11.36) 319/170/28 (61.70/32.88/5.42) 0.00001 0.21 0.88 (0.72 – 1.07)
rs352010 C/T 782/186 (80.79/19.21) 808/226 (78.14/21.86) 0.160 - 0.85 (0.68 – 1.06)
T>C
IL4, T CC/CT/TT 253/192/39 (52.27/39.67/8.06) 306/188/23 (59.19/36.36/4.45) 0.038 0.014 1.33 (1.06 – 1.66)
rs2243250 C/T 698/270 (72.11/27.89) 800/234 (77.37/22.63) 0.003 - 1.32 (1.08 – 1.62)
C>T
IL4, T CC/CT/TT 324/158/2 (66.94/32.64/0.41) 308/183/26 (59.57/35.40/5.03) 0.00001 0.0006 0.66 (0.52 – 0.84)
rs2070874 C/T 806/162 (83.26/16.74) 799/235 (77.27/22.73) 0.00001 - 0.68 (0.55 – 0.85)
C>T
С5, rs17611 A GG/GA/AA 152/231/101 (31.40/47.73/20.87) 171/238/108 (33.08/46.03/20.89) 0.86 0.74 1.03 (0.86 – 1.24)
G>A G/A 535/433 (55.27/44.73) 580/454 (56.09/43.91) 0.744 - 1.03 (0.87 – 1.23)
FAS, G AA/AG/GG 169/214/101 (34.92/44.21/20.87) 156/250/111 (30.17/48.36/21.47) 0.32 0.29 0.91 (0.75 – 1.09)
rs1800682 A/G 552/416 (57.02/42.98) 562/472 (54.35/45.65) 0.247 - 0.90 (0.75 – 1.07)
A>G
IL4RA, G AA/AG/GG 166/206/112 (34.30/42.56/23.14) 163/247/107 (31.53/47.78/20.70) 0.32 0.89 0.99 (0.83 – 1.18)
rs1805010 A/G 538/430 (55.58/44.42) 573/461 (55.42/44.58) 0.798 - 0.99 (0.83 – 1.19)
A>G
TGFb1, T CC/CT/TT 229/201/54 (47.31/41.53/11.16) 222/230/65 (42.94/44.49/12.57) 0.43 0.21 0.88 (0.72 – 1.07)
rs1800469 C/T 659/309 (68.08/31.92) 674/360 (65.18/34.82) 0.185 - 0.88 (0.73 – 1.06)
T>C
a P-value for Chi-square test; P-value for Cochran-Armitage trend test. CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio.
b
The association of IL4 (rs2243250) and COPD in smokers patients and healthy individuals groups (P = 0.00001)
was detected (P = 0.003, OR =1.32 for basic allele test), in (Table 6). Significant association of T-C haplotype by
the log-additive (P =0.014, P cor-FDR =0.019, OR =1.33), and rs2243250 and rs2070874 loci of IL4 gene with COPD
adj
recessive (P =0.036, P cor-FDR =0.041, OR =1.85) models risk in smokers was observed (P =0.024, OR =1.44).
adj
adj
(Tables 3 and 5). The frequency of minor T allele of IL4 The C-T haplotype by rs2243250 and rs2070874 of IL4
(rs2070874) in patients group was decreased (16.74% in gene was identified as protective (P =0.001, OR =0.52;
adj
COPD vs. 22.73% in control P = 0.00001, OR =0.68 for basic Table 6).
allele test). IL4 (rs2070874) was associated with COPD in Association of PPBP (rs352010) with the development
smokers in the log-additive (P =0.0006, P cor-FDR =0.0018, of COPD in smokers was detected in the recessive
adj
OR =0.66) and recessive (P =0.00001, P cor-FDR =7.5 × 10 , (P =0.0008, P =0.002, OR =2.26), and dominant
-5
adj
adj
OR =0.08) models (Table 5). (P =0.0002, P cor-FDR =0.001, OR =0.60) models (Table 5).
cor-FDR
adj
Moderate level of linkage disequilibrium between A significant interaction of the PPBP (rs352010) and
the rs2243250 and rs2070874 loci of IL4 gene was smoking status was detected in the regression analysis
observed (D’ =0.46, r = 0.15) (Figure 1). We have (P interact =0.017, OR =0.60, 95% CI =0.46 – 0.79 in the
2
established significant differences in the haplotype dominant model). PPBP (rs352010) was predominantly
frequencies distribution of IL4 gene loci between associated with COPD in smokers.
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i1.91