Page 34 - GTM-1-1
P. 34
Global Translational Medicine Inflammatory gene-environment interactions in COPD
the main component of the majority of protective gene-
gene combinations associated with COPD in smokers.
The highest risk of COPD was conferred by TT genotype
of PPBP (rs352010) in combination with A allele of FAS
(rs1800682) (OR =3.49).
While in non-smokers, the most commonly featured
was C allele of IL24 (rs291107) in protective patterns and T
allele of IL24 (rs291107) in risk combinations. The highest
risk of COPD in non-smokers was conferred by A allele
of IL12RB2 (rs3762317) together with G allele of IL12A
(rs2243115), C allele of IL4 (rs2070874), and A allele of
IL4RA (rs1805010) (OR =18.5).
The analysis on the gene-gene interaction of
inflammatory gene loci established an association of IL20
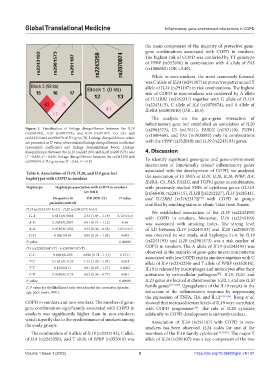
Figure 1. Visualization of linkage disequilibrium between the IL19 (rs2981573), C5 (rs17611), FASLG (rs763110), TGFb1
(rs2243193), IL20 (rs2981573), and IL24 (rs291107) loci (A), and (rs1800469), and FAS (rs1800682) only in combinations
rs2243250 and rs2070874 of IL4 gene (B). Linkage disequilibrium values
are presented as D’ value of normalized linkage disequilibrium coefficient with the PPBP (rs352010) and IL19 (rs2243193) genes.
(Lewontin’s coefficient) and linkage disequilibrium block. Linkage
disequilibrium between the IL19 (rs2243193) and IL20 (rs2981573) was 4. Discussion
2
D’ =0.828, r = 0.458; linkage disequilibrium between the rs2243250 and To identify significant gene-gene and gene-environment
2
rs2070874 of IL4 gene was D’ =0.46, r =0.15.
interactions of functionally related inflammatory genes
associated with the development of COPD, we analyzed
Table 6. Association of IL19, IL20, and IL4 gene loci
haplotypes with COPD in smokers the association of 11 SNPs of IL19, IL20, IL24, PPBP, IL4,
IL4RA, С5, FAS, FASLG, and TGFb1 genes in combination
Haplotype Haplotype association with COPD in smokers with previously studied SNPs of cytokines genes (IL12A
(n=1001) [rs568408, rs2243115], IL12B [rs3212227], IL13 [rs20541),
Frequency in OR (95% CI) P‑value and IL12RB2 [rs3762317]) with COPD in groups
[34]
patients/controls stratified by smoking status in ethnic Tatar from Russia.
IL19 (rs2243193 A>G) - IL20 (rs2981573 A>G) We established association of the IL19 (rs2243193)
G-A 0.6113/0.5081 2.42 (1.84 – 3.18) 2.12×10-6 with COPD in smokers. Moreover, IL19 (rs2243193)
A-G 0.2839/0.2857 0.91 (0.74 – 1.12) 0.36 was associated with smoking index. The strong level
A-A 0.0787/0.1662 0.42 (0.30 – 0.58) 1.07×10-7 of LD between IL19 (rs2243193) and IL20 (rs2981573)
G-G 0.0261/0.04 0.59 (0.34 – 1.03) 0.063 was observed in our study, and haplotype G-A by IL19
P-value 0.00001 (rs2243193) and IL20 (rs2981573) was a risk marker of
IL4 (rs2243250C>T) - (rs2070874C>T) COPD in smokers. The A allele of IL19 (rs2243193) was
C-C 0.6693/0.659 0.896 (0.74 – 1.14) 0.3711 observed in the majority of gene-gene interaction patterns
associated with low COPD risk in smokers together with C
T-C 0.1631/0.1135 1.44 (1.05 – 1.97) 0.024 allele of IL4 (rs2243250) and T allele of PPBP (rs352010).
T-T 0.1076/0.11 0.91 (0.65 – 1.27) 0.6002 IL19 is released by macrophages and monocytes after their
C-T 0.0559/0.1175 0.52 (0.36 – 0.77) 0.001 activation by extracellular pathogens . IL19, IL20, and
[35]
P-value 0.00001 IL24 genes are located at chromosome 1q32.1, and are IL10
P, P value for the likelihood ratio test adjusted for covariates (gender, family genes [14,15,35] . Upregulation of the IL19 results in the
age, pack-years, BMI). reduction of the inflammatory response by suppressing
the expression of TNFA, IL6, and IL12 [14,15,35] . Rong et al.
COPD in smokers and non-smokers. The number of gene- showed that increased serum levels of IL19 were correlated
gene combinations significantly associated with COPD in with COPD progression . The role of IL20 cytokine
[36]
smokers was significantly higher than in non-smokers, subfamily in COPD development is currently unclear.
which is partly due to the predominance of smokers among Association of IL24 (rs291107) with COPD in non-
the study groups.
smokers has been observed. IL24 codes for one of the
The combination of A allele of IL19 (rs2243193), C allele members of the IL10 family cytokines [14,15,35] . The major T
of IL4 (rs2243250), and T allele of PPBP (rs352010) was allele of IL24 (rs291107) was a key component of the two
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i1.91