Page 104 - GTM-4-1
P. 104
Global Translational Medicine Comparative study of Schisandra species on VCI
the target quadrant (P < 0.01) (Figure 3G). In contrast, exhibited a disrupted myelin structure, characterized by
SCF-treated mice demonstrated better spatial learning a loose and disordered myelin sheath and the presence of
and memory ability than the MOD mice, as evidenced by white vacuoles in the corpus callosum (Cc, paramedian),
a significantly increased frequency of platform crossing fimbria of the hippocampus (Fi), ventral posteromedial
(P < 0.05), a higher frequency of target quadrant crossings thalamic nucleus (VPT), and caudate putamen (Cpu,
(P < 0.05), and significantly more time spent in the target striatum) (P < 0.01) (Figure 5). All drug-treated mice
quadrant (P < 0.01). However, the cognitive improvement exhibited significantly preserved white matter integrity
effects of SSF were less pronounced and not statistically (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Notably, the SCF group showed
significant (P > 0.05). In addition, no significant a greater degree of preservation, with denser and more
differences in swimming speed were observed among organized nerve fibers than the SSF group.
groups (P > 0.05) (Figure 3I). Overall, these behavioral The MBP immunohistochemical staining results
assessments demonstrate that SCF treatment significantly (Figure 6) were consistent with the LFB staining data.
ameliorates learning and memory deficits in BCAS mice. Compared with CON mice, the MOD mice exhibited
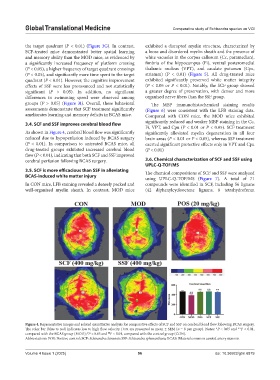
3.4. SCF and SSF improves cerebral blood flow significantly reduced and weaker MBP staining in the Cc,
Fi, VPT, and Cpu (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05). SCF treatment
As shown in Figure 4, cerebral blood flow was significantly significantly alleviated myelin degeneration in all four
reduced due to hypoperfusion induced by BCAS surgery brain areas (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05), whereas SSF treatment
(P < 0.01). In comparison to untreated BCAS mice, all exerted significant protective effects only in VPT and Cpu
drug-treated groups exhibited increased cerebral blood (P < 0.01)
flow (P < 0.01), indicating that both SCF and SSF improved
cerebral perfusion following BCAS surgery. 3.6. Chemical characterization of SCF and SSF using
UPLC-Q-TOF/MS
3.5. SCF is more efficacious than SSF in alleviating The chemical compositions of SCF and SSF were analyzed
BCAS-induced white matter injury
using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS (Figure 7). A total of 71
In CON mice, LFB staining revealed a densely packed and compounds were identified in SCF, including 56 lignans
well-organized myelin sheath. In contrast, MOD mice (42 diphenylcyclooctene lignans, 8 tetrahydrofuran
Figure 4. Representative images and related quantitative analysis for comparative effects of SCF and SSF on cerebral blood flow following BCAS surgery.
The color bar (blue to red) indicates low to high flow velocity. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8 per group). Notes: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01,
compared with the BCAS group (MOD); P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, compared with the control group (CON).
##
#
Abbreviations: POS: Positive control; SCF: Schisandra chinensis; SSF: Schisandra sphenanthera; BCAS: Bilateral common carotid artery stenosis.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 96 doi: 10.36922/gtm.6879