Page 108 - GTM-4-1
P. 108
Global Translational Medicine Comparative study of Schisandra species on VCI
A B C
D E F
G H
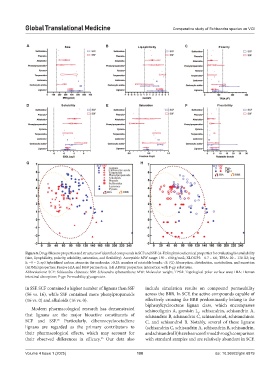
Figure 8. Drug-likeness properties and structures of identified compounds in SCF and SSF. (A-F) Six physicochemical properties for evaluating bioavailability
(size, lipophilicity, polarity, solubility, saturation, and flexibility). Acceptable MW range: 150 – 600 g/moL; XLOGP3: −0.7 – 6.0; TPSA: 20 – 130 Å2; log
S: −9 – 2; sp3 hybridized carbon atoms in the molecule: >0.25; number of rotatable bonds: <9. (G) Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
(ADME) properties: Passive HIA and BBB permeation. (H) ADME properties: Interaction with P-gp substrates.
Abbreviations: SCF: Schisandra chinensis; SSF: Schisandra sphenanthera; MW: Molecular weight; TPSA: Topological polar surface area; HIA: Human
intestinal absorption; P-gp: Permeability glycoprotein.
in SSF. SCF contained a higher number of lignans than SSF include simulation results on compound permeability
(56 vs. 16), while SSF contained more phenylpropanoids across the BBB. In SCF, the active compounds capable of
(16 vs. 0) and alkaloids (16 vs. 0). effectively crossing the BBB predominantly belong to the
biphenylcyclooctene lignan class, which encompasses
Modern pharmacological research has demonstrated schineolignin A, gomisin L , schisandrin, schisandrin A,
2
that lignans are the major bioactive constituents of schisandrin B, schisandrin C, schisanhenol, schisanchinin
SCF and SSF. Particularly, dibenzocyclooctadiene C, and schisandrol B. Notably, several of these lignans
13
lignans are regarded as the primary contributors to (schisandrin C, schisandrin A, schisandrin B, schisandrin,
their pharmacological effects, which may account for and schisandrol B) have been confirmed through comparison
their observed differences in efficacy. Our data also with standard samples and are relatively abundant in SCF.
13
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 100 doi: 10.36922/gtm.6879