Page 106 - GTM-4-1
P. 106
Global Translational Medicine Comparative study of Schisandra species on VCI
A
B C D E
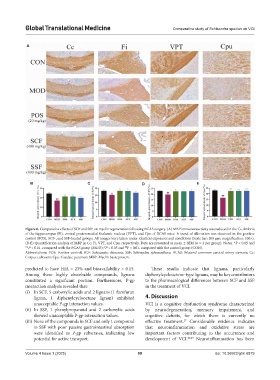
Figure 6. Comparative effects of SCF and SSF on myelin regeneration following BCAS surgery. (A) MBP immunoreactivity was reduced in the Cc, fimbria
of the hippocampus (Fi), ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus (VPT), and Cpu of BCAS mice. A trend of alleviation was observed in the positive
control (POS), SCF-, and SSF-treated groups. All images were taken under identical exposures and conditions (Scale bar: 200 μm; magnification: 100×).
(B-E) Quantification analysis of MBP in Cc, Fi, VPT, and Cpu, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 per group). Notes: *P < 0.05 and
**P < 0.01, compared with the BCAS group (MOD); P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, compared with the control group (CON).
##
#
Abbreviations: POS: Positive control; SCF: Schisandra chinensis; SSF: Schisandra sphenanthera; BCAS: Bilateral common carotid artery stenosis; Cc:
Corpus callosum; Cpu: Caudate putamen; MBP: Myelin basic protein.
predicted to have HIA > 25% and bioavailability > 0.15. These results indicate that lignans, particularly
Among these highly absorbable compounds, lignans diphenylcyclooctene-type lignans, may be key contributors
constituted a significant portion. Furthermore, P-gp to the pharmacological differences between SCF and SSF
interaction analysis revealed that: in the treatment of VCI.
(i) In SCF, 5 carboxylic acids and 2 lignans (1 furofuran
lignan, 1 diphenylcyclooctene lignan) exhibited 4. Discussion
unacceptable P-gp interaction values. VCI is a cognitive dysfunction syndrome characterized
(ii) In SSF, 1 phenylpropanoid and 2 carboxylic acids by neurodegeneration, memory impairment, and
showed unacceptable P-gp interaction values. cognitive deficits, for which there is currently no
(iii) None of the compounds in SCF and only 1 compound effective treatment. Considerable evidence indicates
27
in SSF with poor passive gastrointestinal absorption that neuroinflammation and oxidative stress are
were identified as P-gp substrates, indicating low important factors contributing to the occurrence and
potential for active transport. development of VCI. 28,29 Neuroinflammation has been
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 98 doi: 10.36922/gtm.6879