Page 49 - IJAMD-1-2
P. 49
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
A unified ILKM in smart manufacturing
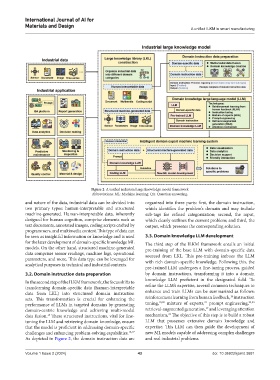
Figure 2. A unified industrial large knowledge model framework
Abbreviations: ML: Machine learning; QA: Question answering.
and nature of the data, industrial data can be divided into organized into three parts: first, the domain instruction,
two primary types: human-interpretable and structured which identifies the problem’s domain and may include
machine-generated. Human-interpretable data, inherently sub-tags for refined categorization; second, the input,
designed for human cognition, comprise elements such as which clearly outlines the current problem; and third, the
text documents, annotated images, coding scripts crafted by output, which presents the corresponding solution.
programmers, and multimedia content. This type of data can
be seen as insightful information or knowledge and is used 3.3. Domain knowledge LLM development
for the later development of domain-specific knowledge ML The third step of the ILKM framework entails an initial
models. On the other hand, structured machine-generated pre-training of the base LLM with domain-specific data
data comprises sensor readings, machine logs, operational sourced from LKL. This pre-training imbues the LLM
parameters, and more. This data type can be leveraged for with rich domain-specific knowledge. Following this, the
analytical purposes in technical and industrial contexts.
pre-trained LLM undergoes a fine-tuning process, guided
3.2. Domain instruction data preparation by domain instructions, transforming it into a domain
knowledge LLM proficient in the designated field. To
In the second step of the ILKM framework, the focus shifts to
transforming domain-specific data (human-interpretable refine the LLM’s expertise, several common techniques to
data from LKL) into structured domain instruction enhance and train LLMs can be summarized as follows:
18
sets. This transformation is crucial for enhancing the reinforcement learning from human feedback, instruction
21
performance of LLMs in targeted domains by generating tuning, 19,20 mixture of experts, prompt engineering, 22,23
17
domain-centric knowledge and achieving multi-modal retrieval-augmented generation, and leveraging attention
24
data fusion. These structured instructions, vital for fine- mechanism, The objective of this step is to build a robust
15
tuning the LLM and retrieving domain knowledge, ensure LLM that possesses extensive domain knowledge and
that the model is proficient in addressing domain-specific expertise. This LLM can then guide the development of
challenges and enhancing problem-solving capabilities. 16,17 new ML models capable of addressing complex challenges
As depicted in Figure 2, the domain instruction data are and real industrial problems.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 43 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.3681