Page 72 - IJAMD-1-2
P. 72
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Machine learning for gel fraction prediction
techniques, decision tree-based techniques, and neural ω x +ω x was replaced with ω x in feature groups 2
P
a
a
P
t
t
networks in predicting the gel fraction was compared. and 3, while ω GelMA x GelMA +ω LAP x LAP -ω PEDOT x PEDOT was
The brief introduction and the tuning parameters for the removed in feature group 2.
models are detailed in the following section.
2.4.2. SVR
2.4.1. LR
The SVR model, a widely used ML regression technique,
The LR technique was selected for its simplicity and was employed to compare its accuracy with the LR
interpretability. LR is ideal for identifying and quantifying model as both are regression-based methods. SVR
linear relationships between inputs and outputs. Its enhances performance over LR in the presence of outliers
straightforward nature provides a baseline model for by maximizing the number of data points within the
comparison with more complex algorithms. In addition, hyperplane area. To achieve a non-LR, the RBF kernel
51
when the relationship between variables is approximately was utilized. The regularization parameter C was set to 993
linear, LR can deliver fast and reliable predictions. The and γ to 0.57 for feature Group 1, while C was 130 and γ
LR model, represented in Equation IV, is fitted using the was 0.53 for feature Groups 2 and 3. The gamma was set to
ordinary least square method. In this work, x GelMA , x LAP , “scale” for all feature groups (1/(n_features * X.var())), and
and x PEDOT are the concentration of GelMA, LAP, and the tolerance for the stopping criterion was 0.001.
PEDOT:SPSS, respectively. x is the UV power intensity, x t
p
is the UV duration, and x is the absorption coefficient. ω 2.4.3. Decision tree regression
a
are the coefficients to be fitted. DTR was selected for its adeptness at mapping complex
y = ω x +ω x -ω x +ω x +ω x +ω decision paths based on input parameters. Unlike
Gel GelMA GelMA LAP LAP PEDOT PEDOT P P t t c
(IV) regression-based techniques, decision trees excel at
B
A
C
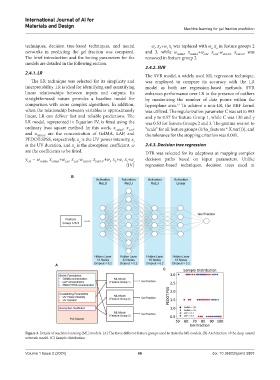
Figure 3. Details of machine learning (ML) models. (A) The three different feature groups used to train the ML models. (B) Architecture of the deep neural
network model. (C) Sample distribution
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 66 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.3807