Page 77 - IJAMD-1-2
P. 77
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Machine learning for gel fraction prediction
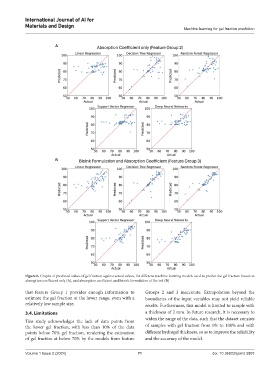
A
B
Figure 6. Graphs of predicted values of gel fraction against actual values, for different machine learning models used to predict the gel fraction based on
absorption coefficient only (A), and absorption coefficient and bioink formulation of the ink (B)
that feature Group 1 provides enough information to Groups 2 and 3 inaccurate. Extrapolation beyond the
estimate the gel fraction at the lower range, even with a boundaries of the input variables may not yield reliable
relatively low sample size. results. Furthermore, this model is limited to sample with
3.4. Limitations a thickness of 2 mm. In future research, it is necessary to
This study acknowledges the lack of data points from widen the range of the data, such that the dataset consists
the lower gel fraction, with less than 10% of the data of samples with gel fraction from 0% to 100% and with
points below 70% gel fraction, rendering the estimation different hydrogel thickness, so as to improve the reliability
of gel fraction at below 70% by the models from feature and the accuracy of the model.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 71 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.3807