Page 66 - IJAMD-1-3
P. 66
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Phase change materials and digital twin technology in thermal energy
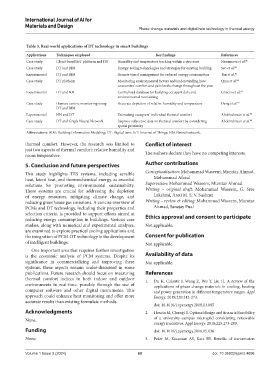
Table 3. Real‑world applications of DT technology in smart buildings
Applications Techniques employed Key findings References
Case study Cloud-based IoT platform and DT Humidity and temperature tracking within a structure Nurumova et al. 86
Case study DT and BIM Energy-saving technologies and strategies for existing building Seo et al. 82
Experimental DT and BIM Remote visual management for reduced energy consumption Tan et al. 83
Case study DT platform Monitoring environmental factors and understanding how Qian et al. 84
consumers’ comfort and pain levels change throughout the year
Experimental DT and NN Centralized database for building occupant data and Gnecco et al. 87
environmental monitoring
Case study Human-centric monitoring using Accurate depiction of relative humidity and temperature Deng et al. 85
DT and BIM
Experimental NN and DT Estimating occupiers’ individual thermal comfort Abdelrahman et al. 88
Case study DT and Graph Neural Network Improve subjective data on thermal comfort by considering Abdelrahman et al. 89
spatial proximity
Abbreviations: BIM: Building Information Modeling; DT: Digital twin; IoT: Internet of Things; NN: Neural network.
thermal comfort. However, the research was limited to Conflict of interest
just two aspects of thermal comfort: relative humidity and
room temperature. The authors declare they have no competing interests.
5. Conclusion and future perspectives Author contributions
This study highlights TES systems, including sensible Conceptualization: Mohammad Waseem, Mumtaz Ahmad,
heat, latent heat, and thermochemical energy, as essential Mohammad Afazal
solutions for promoting environmental sustainability. Supervision: Mohammad Waseem, Mumtaz Ahmad
These systems are crucial for addressing the depletion Writing – original draft: Mohammad Waseem, G. Sree
of energy resources, mitigating climate change, and Lakshmi, Areti M. S. V. Sushma
reducing greenhouse gas emissions. A concise overview of Writing – review & editing: Mohammad Waseem, Mumtaz
PCMs and DT technology, including their properties and Ahmad, Sanajay Pual
selection criteria, is provided to support efforts aimed at Ethics approval and consent to participate
reducing energy consumption in buildings. Various case
studies, along with numerical and experimental analyses, Not applicable.
are examined to explore practical cooling applications and
the integration of PCM-DT technology in the development Consent for publication
of intelligent buildings. Not applicable.
One important area that requires further investigation
is the economic analysis of PCM systems. Despite its Availability of data
significance in commercializing and improving these Not applicable.
systems, these aspects remain under-discussed in some
publications. Future research should focus on measuring References
thermal comfort indices in both indoor and outdoor 1. Du K, Calautit J, Wang Z, Wu Y, Liu H. A review of the
environments in real-time, possibly through the use of applications of phase change materials in cooling, heating
computer software and other digital instruments. This and power generation in different temperature ranges. Appl
approach could enhance heat monitoring and offer more Energy. 2018;220:242-273.
accurate results than existing formulaic methods.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.03.005
Acknowledgments 2. Husein M, Chung IY. Optimal design and financial feasibility
None. of a university campus microgrid considering renewable
energy incentives. Appl Energy. 2018;225:273-289.
Funding doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.05.036
None. 3. Peker M, Kocaman AS, Kara BY. Benefits of transmission
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 60 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.4696