Page 76 - IJAMD-1-3
P. 76
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Review of gas turbine blade failures by erosion
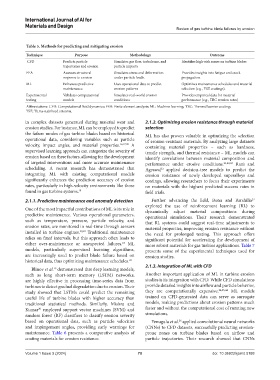
Table 5. Methods for predicting and mitigating erosion
Technique Purpose Methodology Outcome
CFD Predicts particle Simulates gas flow, turbulence, and Identifies high-risk zones on turbine blades
trajectories and erosion particle impacts
FEA Assesses structural Simulates stress and deformation Provides insights into fatigue and crack
response to erosion under particle loads. propagation.
ML Enhances predictive Uses operational data to predict Optimizes maintenance schedules and material
maintenance. erosion patterns selection (e.g., YSZ coatings).
Experimental Validates computational Simulates real-world erosion Provides empirical data for material
testing models conditions performance (e.g., TBC erosion rates)
Abbreviations: CFD: Computational fluid dynamics; FEA: Finite element analysis; ML: Machine learning; TBC: Thermal barrier coating;
YSZ: Yttria-stabilized zirconia.
in complex datasets generated during material wear and 2.1.2. Optimizing erosion resistance through material
erosion studies. For instance, ML can be employed to predict selection
the failure modes of gas turbine blades based on historical ML has also proven valuable in optimizing the selection
operational data, considering variables such as particle of erosion-resistant materials. By analyzing large datasets
velocity, impact angles, and material properties. 16,17,38 A containing material properties – such as hardness,
supervised learning approach can categorize the severity of tensile strength, and thermal resistance – ML models can
erosion based on these factors, allowing for the development identify correlations between material composition and
of targeted interventions and more accurate maintenance performance under erosive conditions. 21,42,43 Rani and
scheduling. A recent research has demonstrated that Agrawal applied decision-tree models to predict the
22
integrating ML with existing computational models erosion resistance of newly developed superalloys and
significantly enhances the prediction accuracy of erosion coatings, allowing researchers to focus their experiments
rates, particularly in high-velocity environments like those on materials with the highest predicted success rates in
found in gas turbine systems. 18 field trials.
23
2.1.1. Predictive maintenance and anomaly detection Further advancing the field, Bonu and Barshilia
explored the use of reinforcement learning (RL) to
One of the most impactful contributions of ML is its role in dynamically adjust material compositions during
predictive maintenance. Various operational parameters, operational simulations. Their research demonstrated
such as temperature, pressure, particle velocity, and that RL systems could suggest real-time adjustments to
erosion rates, are monitored in real-time through sensors material properties, improving erosion resistance without
installed in turbine engines. 39,40 Traditional maintenance the need for prolonged testing. This approach offers
relies on fixed intervals, but this approach often leads to significant potential for accelerating the development of
either over-maintenance or unexpected failures. ML more robust materials for gas turbine applications. Table 7
18
models, particularly supervised learning algorithms, presents some of the experimental techniques used for
are increasingly used to predict blade failure based on erosion studies.
historical data, thus optimizing maintenance schedules. 41
2.1.3. Integration of ML with CFD
Blinov et al. demonstrated that deep learning models,
19
such as long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, Another important application of ML in turbine erosion
are highly effective in processing time-series data from studies is its integration with CFD. While CFD simulations
turbines to detect gradual degradation due to erosion. Their provide detailed insights into airflow and particle behavior,
study showed that LSTMs could predict the remaining they are computationally expensive. 24,25,44 ML models
useful life of turbine blades with higher accuracy than trained on CFD-generated data can serve as surrogate
traditional statistical methods. Similarly, Mishra and models, making predictions about erosion patterns much
Kumar employed support vector machines (SVM) and faster and without the computational cost of running new
20
random forest (RF) classifiers to classify erosion severity simulations.
based on operational data, such as particle velocities Yenugula et al. applied convolutional neural networks
26
and impingement angles, providing early warnings for (CNNs) to CFD datasets, successfully predicting erosion-
maintenance. Table 6 presents a comparative analysis of prone zones on turbine blades based on airflow and
coating materials for erosion resistance. particle trajectories. Their research showed that CNNs
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 70 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.5188