Page 77 - IJAMD-1-3
P. 77
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Review of gas turbine blade failures by erosion
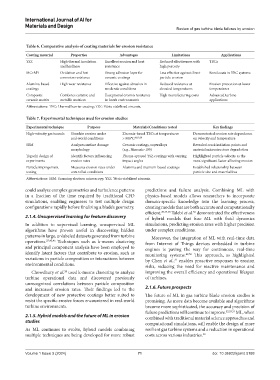
Table 6. Comparative analysis of coating materials for erosion resistance
Coating material Properties Advantages Limitations Applications
YSZ High thermal insulation Excellent erosion and heat Reduced effectiveness with TBCs
and hardness resistance high porosity
MCrAlY Oxidation and hot Strong adhesion layer for Less effective against direct Bond coats in TBC systems
corrosion resistance ceramic coatings particle erosion
Alumina-based High wear resistance Effective against abrasion in Reduced resistance at Erosion protection at lower
coatings moderate conditions elevated temperatures temperatures
Composite Combines ceramic and Exceptional erosion resistance High manufacturing costs Advanced turbine
ceramic matrix metallic matrices in harsh environments applications
Abbreviations: TBC: Thermal barrier coating; YSZ: Yttria-stabilized zirconia.
Table 7. Experimental techniques used for erosion studies
Experimental technique Purpose Materials/Conditions tested Key findings
High-velocity gas tunnels Simulate erosion under Zirconia-based TBCs at temperatures Demonstrated erosion rate dependence
real-world conditions > 980°C 16,19,20 on velocity and temperature
SEM Analyzes surface damage Ceramic coatings, superalloys Revealed crack initiation points and
morphology (e.g., Nimonic-105) material microstructure degradation
Taguchi design of Identify factors influencing Plasma-sprayed YSZ coatings with varying Highlighted particle velocity as the
experiments erosion rates impact angles most significant factor affecting erosion
Particle impingement Measures erosion rates under Alumina and titanium-based coatings Established relationship between
testing controlled conditions particle size and material loss
Abbreviations: SEM: Scanning electron microscopy; YSZ: Yttria-stabilized zirconia.
could analyze complex geometries and turbulence patterns predictions and failure analysis. Combining ML with
in a fraction of the time required by traditional CFD physics-based models allows researchers to incorporate
simulations, enabling engineers to test multiple design domain-specific knowledge into the learning process,
configurations rapidly before finalizing a blade’s geometry. creating models that are both accurate and computationally
efficient. 29,47,48 Talebi et al. demonstrated the effectiveness
30
2.1.4. Unsupervised learning for feature discovery of hybrid models that fuse ML with fluid dynamics
In addition to supervised learning, unsupervised ML simulations, predicting erosion rates with higher precision
algorithms have proven useful in discovering hidden under complex conditions.
patterns in large, unlabeled datasets generated from turbine Moreover, the integration of ML with real-time data
operations. 27,45,46 Techniques such as k-means clustering from Internet of Things devices embedded in turbine
and principal component analysis have been employed to engines is paving the way for continuous, real-time
identify latent factors that contribute to erosion, such as monitoring systems. 49,50 This approach, as highlighted
variations in particle composition or interactions between by Chen et al., enables proactive responses to erosion
31
environmental conditions. risks, reducing the need for reactive maintenance and
Chowdhury et al. used k-means clustering to analyze improving the overall efficiency and operational lifespan
28
turbine operational data and discovered previously of turbines.
unrecognized correlations between particle composition
and increased erosion rates. Their findings led to the 2.1.6. Future prospects
development of new protective coatings better suited to The future of ML in gas turbine blade erosion studies is
resist the specific erosive forces encountered in real-world promising. As more data become available and algorithms
turbine environments. become more sophisticated, the accuracy and precision of
failure predictions will continue to improve. 32,33,51 ML, when
2.1.5. Hybrid models and the future of ML in erosion combined with traditional material science approaches and
studies computational simulations, will enable the design of more
As ML continues to evolve, hybrid models combining resilient gas turbine systems and a reduction in operational
multiple techniques are being developed for more robust costs across various industries. 52
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 71 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.5188