Page 51 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 51
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
ML-based MPC for multizone BAC
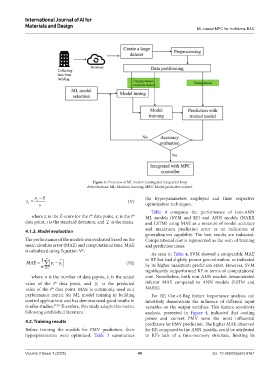
Figure 3. Overview of ML model training and integration loop
Abbreviations: ML: Machine learning; MPC: Model predictive control.
x x the hyperparameters employed and their respective
z i s (V) optimization techniques.
i
Table 4 compares the performance of non-ANN
where z is the Z-score for the i data point, x is the i ML models (SVM and RF) and ANN models (NARX
th
th
i
i
data point, s is the standard deviation, and x is the mean. and LSTM) using MAE as a measure of model accuracy
4.1.3. Model evaluation and maximum prediction error as an indication of
generalization capability. The best results are indicated.
The performance of the models was evaluated based on the Computational cost is represented as the sum of training
mean absolute error (MAE) and computational time. MAE and prediction times.
is calculated using Equation VI:
As seen in Table 4, SVM showed a comparable MAE
1 n to RF but had slightly poorer generalization, as indicated
MAE y y (VI)
n i1 i i by its higher maximum prediction error. However, SVM
significantly outperformed RF in terms of computational
where n is the number of data points, y is the actual cost. Nonetheless, both non-ANN models demonstrated
i
value of the i data point, and y is the predicted inferior MAE compared to ANN models (LSTM and
th
i
value of the i data point. MAE is commonly used as a NARX).
th
performance metric for ML model training in building For RF, Out-of-Bag feature importance analysis can
control applications and has demonstrated good results in intuitively demonstrate the influence of different input
similar studies. 37,38 Therefore, this study adopts this metric variables on the output variables. This feature sensitivity
following established literature. analysis, presented in Figure 4, indicated that cooling
power and current PMV were the most influential
4.2. Training results predictors for PMV prediction. The higher MAE observed
Before training the models for PMV prediction, their for RF, compared to the ANN models, could be attributed
hyperparameters were optimized. Table 3 summarizes to RF’s lack of a time-memory structure, limiting its
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 45 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.8161