Page 83 - IJB-1-1
P. 83
Libiao Liu and Xiaohong Wang
mainly two branches, with only a few branches that
are trigeminal. It is very hard for the CCO method to
mimic the natural vascular systems completely. The
dichotomous branching can be determined as the basic
structure of biomimetic vessel. Based on the physical
laws and conditions to establish the corresponding
model tree, as shown in Figure 1, the optimization
principle is to make sure the vascular system
throughout the entire organ as far as possible and
reduce the length of the vessels to improve its
efficiency. In the optimization design, the first step is
mainly to build a larger trunk, and based on it,
increase new blood vessels as a subordinate branch; at
the same time, the start and the end of each segment of
the vessel and its vessel diameter are determined. Af-
ter a series of deduction, an entire vascular system can
be built.
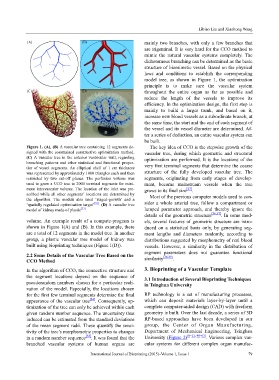
Figure 1. (A), (B) A vascular tree containing 12 segments de- The key idea of CCO is the stepwise growth of the
signed with the constrained constructive optimization method. vascular tree, during which geometric and structural
(C) A vascular tree in the anterior ventricular wall, regarding optimization are performed. It is the locations of the
branching patterns and other statistical and functional proper-
ties of vessel segments. An elliptical shell of 1 cm thickness very first terminal segments that determine the coarse
was represented by approximately 1000 triangles each and then structure of the fully developed vascular tree. The
restricted by two cut-off planes. The perfusion volume was segments, originating from early stages of develop-
used to grow a CCO tree to 2000 terminal segments for mini- ment, become mainstream vessels when the tree
mum intravascular volume. The location of the inlet was pre- grows to its final size [27] .
scribed while all other segments’ locations are determined by
the algorithm. The models also used ‘staged-growth’ and a Most of the previous computer models used to con-
‘spatially regulated optimization target’ [32] . (D) A vascular tree sider a whole arterial tree, follow a compartment or
model of kidney made of plastic [33] . lumped parameter approach, and thereby ignore the
details of the geometric structure [36,37] . In some mod-
volume. An example result of a compute-program is els, several features of geometric structure are intro-
shown in Figure 1(A) and (B). In this example, there duced on a statistical basis only, by generating seg-
are a total of 12 segments in the model tree. In another ment lengths and diameters randomly, according to
group, a plastic vascular tree model of kidney was distributions suggested by morphometry of real blood
built using bioprinting techniques (Figure 1(D)). vessels. However, a similarity in the distribution of
segment parameters does not guarantee functional
2.2 Some Details of the Vascular Tree Based on the [38,39]
CCO Method similarity .
In the algorithm of CCO, the connective structure and 3. Bioprinting of a Vascular Template
the segment locations depend on the sequence of 3.1 Introduction of Several Bioprinting Techniques
pseudorandom numbers chosen for a particular reali- in Tsinghua University
zation of the model. Especially, the locations chosen
for the first few terminal segments determine the final RP technology is a set of manufacturing processes,
appearance of the vascular tree [34] . Consequently, op- which can deposit materials layer-by-layer until a
timization of the tree can only be achieved within each complete computer-aided design (CAD) with freeform
given random number sequence. The uncertainty thus geometry is built. Over the last decade, a series of 3D
induced can be estimated from the standard deviations RP-based approaches have been developed in our
of the mean segment radii. These quantify the sensi- group, the Center of Organ Manufacturing,
tivity of the tree’s morphometric properties to changes Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua
in a random number sequence [35] . It was found that the University (Figure 2) [8–11, 40–63] . Various complex vas-
branched vascular systems of human organs are cular systems for different complex organ manufac-
International Journal of Bioprinting (2015)–Volume 1, Issue 1 79