Page 477 - IJB-10-1
P. 477
International Journal of Bioprinting TPMS bone scaffold
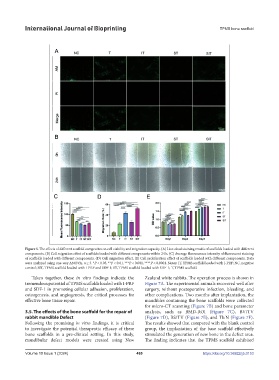
Figure 5. The effects of different scaffold composites on cell viability and migration capacity. (A) Live-dead staining results of scaffolds loaded with different
components. (B) Cell migration effect of scaffolds loaded with different components within 24 h. (C) Average fluorescence intensity of fluorescent staining
of scaffolds loaded with different components. (D) Cell migration effect. (E) Cell proliferation effect of scaffolds loaded with different components. Data
were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, n ≥ 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Notes: IT, TPMS scaffold loaded with I-PRF; NC, negative
control; SIT, TPMS scaffold loaded with I-PRF and SDF-1; ST, TPMS scaffold loaded with SDF-1; T, TPMS scaffold.
Taken together, these in vitro findings indicate the Zealand white rabbits. The operation process is shown in
tremendous potential of TPMS scaffolds loaded with I-PRF Figure 7A. The experimental animals recovered well after
and SDF-1 in promoting cellular adhesion, proliferation, surgery, without postoperative infection, bleeding, and
osteogenesis, and angiogenesis, the critical processes for other complications. Two months after implantation, the
effective bone tissue repair. mandibles containing the bone scaffolds were collected
for micro-CT scanning (Figure 7B) and bone parameter
3.5. The effects of the bone scaffold for the repair of analysis, such as BMD-ROI (Figure 7C), BV/TV
rabbit mandible Defect (Figure 7D), BS/TV (Figure 7E), and Tb.N (Figure 7F).
Following the promising in vitro findings, it is critical The results showed that compared with the blank control
to investigate the potential therapeutic efficacy of these group, the implantation of the base scaffold effectively
bone scaffolds in a pre-clinical setting. In this study, stimulated the generation of new bone in the defect area.
mandibular defect models were created using New The finding indicates that the TPMS scaffold exhibited
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 469 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0153