Page 367 - IJB-10-2
P. 367
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for vascular regeneration
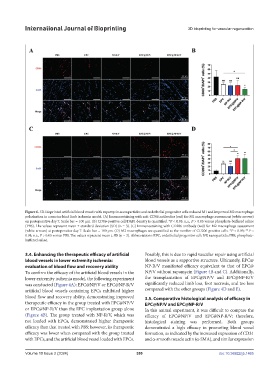
Figure 6. 3D-bioprinted artificial blood vessels with rapamycin-nanoparticles and endothelial progenitor cells reduced M1 and improved M2 macrophage
polarization in a murine hind limb ischemia model. (A) Immunostaining with anti-CD86 antibodies (red) for M1 macrophage assessment (white arrows)
on postoperative day 7. Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) CD86-positive cell/DAPI density is quantified. *P < 0.05; n.s., P > 0.05 versus phosphate-buffered saline
(PBS). The values represent mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). (C) Immunostaining with CD206 antibody (red) for M2 macrophage assessment
(white arrows) at postoperative day 7. Scale bar = 100 µm. (D) M2 macrophages are quantified as the number of CD206-positive cells. *P < 0.05; **P <
0.01; n.s., P > 0.05 versus PBS. The values represent mean ± SD (n = 3). Abbreviations: EPC, endothelial progenitor cell; NP, nanoparticle; PBS, phosphate-
buffered saline.
3.4. Enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of artificial Possibly, this is due to rapid vascular repair using artificial
blood vessels in lower extremity ischemia: blood vessels as a supportive structure. Ultimately, EPC@
evaluation of blood flow and recovery ability NP-R/V manifested efficacy equivalent to that of EPC@
To confirm the efficacy of the artificial blood vessels in the NP/V without rapamycin (Figure 4B and C). Additionally,
lower extremity ischemia model, the following experiment the transplantation of EPC@NP/V and EPC@NP-R/V
was conducted (Figure 4A): EPC@NP/V or EPC@NP-R/V significantly reduced limb loss, foot necrosis, and toe loss
artificial blood vessels containing EPCs exhibited higher compared with the other groups (Figure 4D and E).
blood flow and recovery ability, demonstrating improved 3.5. Comparative histological analysis of efficacy in
therapeutic efficacy in the group treated with EPC@NP/V EPC@NP/V and EPC@NP-R/V
or EPC@NP-R/V than the EPC implantation group alone In this animal experiment, it was difficult to compare the
(Figure 4B). The group treated with NP-R/V, which was efficacy of EPC@NP/V and EPC@NP-R/V; therefore,
not loaded with EPCs, demonstrated higher therapeutic histological staining was performed. Both groups
efficacy than that treated with PBS; however, its therapeutic demonstrated a high efficacy in promoting blood vessel
efficacy was lower when compared with the group treated formation, as indicated by the increased expression of CD31
with EPCs, and the artificial blood vessel loaded with EPCs. and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and similar expression
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 359 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1465