Page 399 - IJB-10-2
P. 399
International Journal of Bioprinting Automated bioink mixer improves bioprinting
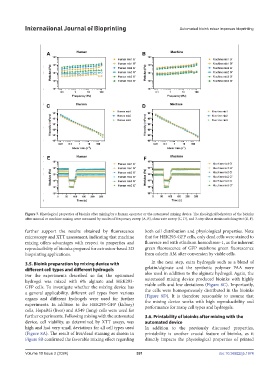
Figure 7. Rheological properties of bioinks after mixing by a human operator or the automated mixing device. The rheological behaviors of the bioinks
after manual or machine mixing were measured by modes of frequency sweep (A, B), shear rate sweep (C, D), and 3-step shear strain switching test (E, F).
further support the results obtained by fluorescence both cell distribution and physiological properties. Note
microscopy and XTT assessment, indicating that machine that for HEK293-GFP cells, only dead cells were stained to
mixing offers advantages with respect to properties and fluoresce red with ethidium homodimer-1, as the inherent
reproducibility of bioinks prepared for extrusion-based 3D green fluorescence of GFP outshone green fluorescence
bioprinting applications. from calcein AM after conversion by viable cells.
3.5. Bioink preparation by mixing device with In the next step, extra hydrogels such as a blend of
different cell types and different hydrogels gelatin/alginate and the synthetic polymer PAA were
For the experiments described so far, the optimized also used in addition to the alginate hydrogel. Again, the
hydrogel was mixed with 6% alginate and HEK293- automated mixing device produced bioinks with highly
GFP cells. To investigate whether the mixing device has viable cells and low deviations (Figure 8C). Importantly,
a general applicability, different cell types from various the cells were homogeneously distributed in the bioinks
(Figure 8D). It is therefore reasonable to assume that
organs and different hydrogels were used for further the mixing device works with high reproducibility and
experiments. In addition to the HEK293-GFP (kidney) performance for many cell types and hydrogels.
cells, HepaRG (liver) and A549 (lung) cells were used for
further experiments. Following mixing with the automated 3.6. Printability of bioinks after mixing with the
device, cell viability, as determined by XTT assays, was automated device
high and had very small deviations for all cell types used In addition to the previously discussed properties,
(Figure 8A). The result of live/dead staining as shown in printability is another crucial feature of bioinks, as it
Figure 8B confirmed the favorable mixing effect regarding directly impacts the physiological properties of printed
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 391 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1974