Page 64 - IJB-10-2
P. 64
International Journal of Bioprinting Advancements in 3D printing
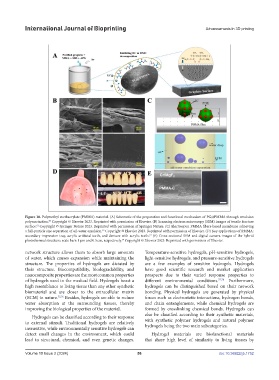
Figure 10. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) material. (A) Schematic of the preparation and functional mechanism of PG@PMMA through emulsion
60
polymerization. Copyright © Elsevier 2023. Reprinted with permission of Elsevier. (B) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of tensile fracture
61
surface. Copyright © Springer Nature 2023. Reprinted with permission of Springer Nature. (C) Electrospun PMMA fibers-based membrane achieving
62
a full-particle size separation of oil-water emulsion. Copyright © Elsevier 2023. Reprinted with permission of Elsevier. (D) Key applications of PMMA:
secondary impression tray, acrylic artificial teeth, and denture with acrylic teeth. (E) Cross-sectional SEM and digital camera images of the hybrid
63
64
photothermal structure; scale bars: 1 µm and 0.5 cm, respectively. Copyright © Elsevier 2023. Reprinted with permission of Elsevier.
network structure allows them to absorb large amounts Temperature-sensitive hydrogels, pH-sensitive hydrogels,
of water, which causes expansion while maintaining the light-sensitive hydrogels, and pressure-sensitive hydrogels
structure. The properties of hydrogels are dictated by are a few examples of sensitive hydrogels. Hydrogels
their structure. Biocompatibility, biodegradability, and have good scientific research and market application
nanocomposite properties are the most common properties prospects due to their varied response properties to
of hydrogels used in the medical field. Hydrogels boast a different environmental conditions. 77,78 Furthermore,
high resemblance to living tissue than any other synthetic hydrogels can be distinguished based on their network
biomaterial and are closer to the extracellular matrix bonding. Physical hydrogels are generated by physical
(ECM) in nature. 75,76 Besides, hydrogels are able to reduce forces such as electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds,
water absorption at the surrounding tissues, thereby and chain entanglements, while chemical hydrogels are
improving the biological properties of the material. formed by crosslinking chemical bonds. Hydrogels can
Hydrogels can be classified according to their response also be classified according to their synthetic materials,
to external stimuli. Traditional hydrogels are relatively with synthetic polymer hydrogels and natural polymer
insensitive, while environmentally sensitive hydrogels can hydrogels being the two main subcategories.
detect small changes in the environment, which could Hydrogel materials are biofunctional materials
lead to structural, chemical, and even genetic changes. that share high level of similarity to living tissues by
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 56 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1752