Page 55 - IJB-3-2
P. 55
Pujiang Shi, et. al.
tion patterns on the ultrathin membrane (Figure 3); the
cells remain inside the bioprinting droplets at the first
24 hours and subsequently the cells migrate, proliferate
and gradually occupy the gap among each droplet, until
finally an intact ARPE-19 cell monolayer is formed on
the ultrathin membrane. The high quality of ARPE-19
cell monolayer is verified by confocal microscopy and
by HE and ZO-1 staining. The cells cover the whole
mem brane, and no vacant area is observed (Figure 4 ). In
the confocal image, the actin staining indicates intense
interactions among cells, while DAPI staining (cell
nucleus in blue) proves that no overlaid cells are in the
cell layer (Figure 5). Thus, a high quality ARPE-19 cell
monolayer is created on the ultrathin membrane.
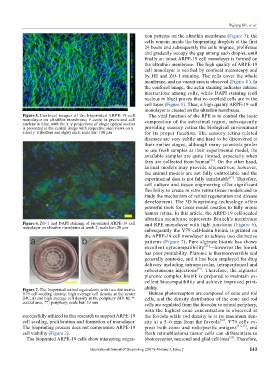
Figure 5. Confocal images of the bioprinted ARPE-19 cell The vital function of the RPE is to control the ionic
monolayer on ultrathin membrane; F-actin in green and cell
nucleus in blue, with the x–y projections of single optical section composition of the subretinal region, subsequently
is presented in the central image with respective side-views on x– providing sensory retina the biological environment
z and y–z (bottom and right) axes; scale bar: 100 µm for its proper function. The sensory retina-related
diseases are very subtle and hard to be discovered at
their earlier stages; although many scientists prefer
to use fresh samples as their experimental model, the
available samples are quite limited, especially when
they are collected from human [26] . On the other hand,
animal models may provide alternatives; however,
the animal models are not fully controllable and the
[27]
experimental data is not fully translatable . Therefore,
cell culture and tissue engineering offer significant
flexi bility to create in vitro retina tissue models and to
study the mechanism of retinal regeneration and disease
development. The 3D bioprinting technology offers
powerful tools for tissue model creation to fully mimic
human retina. In this article, the ARPE-19 cell-seeded
ultrathin membrane represents Brunch’s membrane
Figure 6. ZO-1 and DAPI staining of bioprinted ARPE-19 cell and RPE monolayer with tight junctions (Figure 6),
monolayer on ultrathin membrane at week 2; scale bar: 20 µm
subsequently the Y79 cell-laden bioink is printed on
the APRE-19 cell monolayer to achieve two distinctive
patterns (Figure 7). Pure alginate bioink has shown
excellent cytocompatibility [28] —however the bioink
has poor printability. Pluronic is thermoreversible and
generally nontoxic, and it has been employed for drug
delivery including intramuscular, intraperitoneal and
subcutaneous injections [29] . Therefore, the alginate/
pluronic complex bioink is prepared to maintain ex-
cellent biocompatibility and achieve improved print-
Figure 7. The bioprinted retinal equivalents with two distinctive ability.
Y79 cell-seeding density: high average cell density at the center Human photoreceptors are composed of cone and rod
(HC, a) and high average cell density at the periphery (HP, b); *: cells, and the density distribution of the cone and rod
central area, **: periphery; scale bar: 10 mm cells are regulated from the foveolar to retinal periphery,
with the highest cone concentration is observed at
successfully utilized in this research to support ARPE-19 the foveola while rod density is at its maximum den-
cell seeding, proliferation and formation of monolayer. sity at a 5–6 mm from the foveola [30] . Y79 cells ex-
The bioprinting process does not compromise ARPE-19 press both cone- and rod-specific antigens [31–33] , and
cell viability (Figure 2). fresh retinoblastoma tumor cells can differentiate to
The bioprinted ARPE-19 cells show interesting migra- photoreceptor, neuronal and glial cell lines . Therefore,
[34]
International Journal of Bioprinting (2017)–Volume 3, Issue 2 143