Page 263 - IJB-10-3
P. 263
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting organoids for toxicity testing
and MPTA at low dosages was tolerable in DOs derived verify the representativeness of the genetic characteristics
from healthy donor hiPSC, suggesting that PS-MPs and of ALD.
TBBPA at environmental concentrations lower than those Briefly, hiPSC-AC19-derived AC19_HE-P3 and AC19_
used in this study might be tolerable for healthy individuals. EPC-P4, together with LX-2, were printed and assembled
These findings were distinct from those reported in a prior into highly viable AC19_DOs with increasing expression
study that utilized human embryonic stem cell-derived of respective specific gene in the hydrogel microspheres
hepatocyte organoids, which showed cytotoxicity, lipid (Figure S4A–C). After co-culture, multicellular AC19_DOs
metabolism, and gene transcriptional toxicity even at maturely expressed endothelial cell and hepatocyte markers
37
lower concentrations of 250 ng/mL. We speculated that (CD31/MRP2) (Figure S4D in Supplementary File).
hydrogel encapsulation and multicellular constituents To investigate whether AC19_DOs represented
might have altered the toxic response of organoids. an inherited feature of ALD, we conducted qRT-PCR
and RNA-seq analysis to compare the transcriptional
3.4. DOs with ALD genetic backgrounds exhibited
disease-related gene phenotypes expression levels of ALD biomarkers between AC19_DOs
and DOs derived from healthy donor hiPSCs (N_DOs)
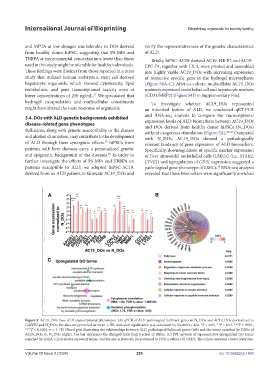
Pollutants, along with genetic susceptibility to the disease without exogenous stimulation (Figure 5A). 40-42 Compared
and alcohol stimulation, may contribute to the development with N_DOs, AC19_DOs showed a pathologically
of ALD through their synergistic effects. hiPSCs from relevant tendency of gene expression of ALD biomarkers.
38
patients with liver diseases carry a personalized genetic Specifically, downregulation of specific marker expression
39
and epigenetic background of the diseases. In order to of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) (i.e., STAB2,
further investigate the effects of PS-MPs and TBBPA on LYVE1) and upregulation of CD31 expression suggested a
patients susceptible to ALD, we adopted hiPSC-AC19, pathological gene phenotype of LSECs. RNA-seq analysis
43
derived from an ALD patient, to fabricate AC19_DOs and revealed that these biomarkers were significantly enriched
Figure 5. AC19_DOs have ALD transcriptional phenotypes. (A) qPCR of ALD pathological hallmark genes in N_DOs and AC19_DOs normalized to
GAPDH and N_DOs; the data are presented as mean ± SD; statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001,
****P < 0.0001, n = 3. (B) Chord plot illustrating the relationships between ALD pathological hallmark genes (left) and the terms enriched by DEGs of
AC19_DOs vs. N_DOs (right). The bar represents the changed folds (log10 scale) of DEGs. (C) PPI network of representative upregulated GO terms
enriched by GSEA. Circle nodes represent terms, and the size is inversely proportional to FDR q-values (all <0.25). The colors represent cluster identities.
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 255 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1403