Page 535 - IJB-10-3
P. 535
International Journal of Bioprinting Mechanical responses of 3D-printed AFO
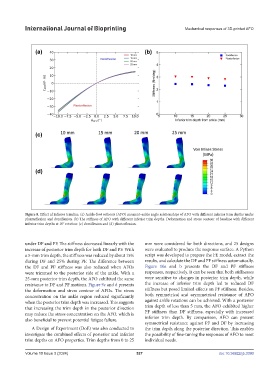
Figure 8. Effect of inferior trimline. (a) Ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) moment–ankle angle relationships of AFO with different inferior trim depths under
plantarflexion and dorsiflexion. (b) The stiffness of AFO with different inferior trim depths. Deformation and stress contour of baseline with different
inferior trim depths at 10° rotation: (c) dorsiflexion and (d) plantarflexion.
under DF and PF. The stiffness decreased linearly with the mm were considered for both directions, and 25 designs
increase of posterior trim depth for both DF and PF. With were evaluated to produce the response surface. A Python
a 5-mm trim depth, the stiffness was reduced by about 15% script was developed to prepare the FE model, extract the
during DF and 25% during PF. The difference between results, and calculate the DF and PF stiffness automatically.
the DF and PF stiffness was also reduced when AFOs Figure 10a and b presents the DF and PF stiffness
were trimmed to the posterior side of the ankle. With a responses, respectively. It can be seen that both stiffnesses
25-mm posterior trim depth, the AFO exhibited the same were sensitive to changes in posterior trim depth, while
resistance to DF and PF motions. Figure 9c and d presents the increase of inferior trim depth led to reduced DF
the deformation and stress contour of AFOs. The stress stiffness but posed limited effects on PF stiffness. Besides,
concentration on the ankle region reduced significantly both symmetrical and asymmetrical resistance of AFO
when the posterior trim depth was increased. This suggests against ankle rotations can be achieved. With a posterior
that increasing the trim depth in the posterior direction trim depth of less than 5 mm, the AFO exhibited higher
may reduce the stress concentration on the AFO, which is PF stiffness than DF stiffness, especially with increased
also beneficial to prevent potential fatigue failure. inferior trim depth. By comparison, AFO can present
symmetrical resistance against PF and DF by increasing
A Design of Experiment (DoE) was also conducted to the trim depth along the posterior direction. This enables
investigate the combined effects of posterior and inferior the possibility of fine-tuning the responses of AFO to meet
trim depths on AFO properties. Trim depths from 0 to 25 individual needs.
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 527 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3390