Page 111 - IJB-4-2
P. 111
Physical stimulations and their osteogenesis-inducing mechanisms
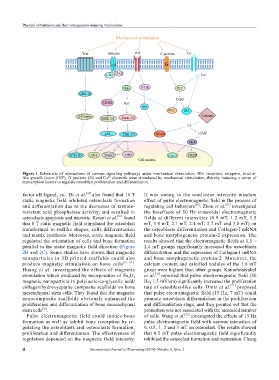
Figure 1. Schematic of interactions of various signaling pathways under mechanical stimulation. Wnt receptors, integrins, insulin-
like growth factor (IGF), G proteins (G) and Ca channels were stimulated by mechanical stimulation, thereby inducing a series of
2+
transcription factors to regulate osteoblast proliferation and differentiation.
factor κB ligand, etc. Di et al. [64] also found that 16 T It was owing to the nonlinear intensity window
static magnetic field inhibited osteoclasts formation effect of pulse electromagnetic field in the process of
and differentiation due to the decreases of tartrate- regulating cell behaviors [68] . Zhou et al. [69] investigated
resistant acid phosphatase activity, and resulted in the bioeffects of 50 Hz sinusoidal electromagnetic
[36]
osteoclasts apoptosis and necrosis. Kotani et al. found fields at different intensities (0.9 mT, 1.2 mT, 1.5
that 8 T static magnetic field stimulated the osteoblast mT, 1.8 mT, 2.1 mT, 2.4 mT, 2.7 mT and 3.0 mT) on
transformed to rodlike shapes, cells differentiation the osteoblasts differentiation and Collagen-I mRNA
and matrix synthesis. Moreover, static magnetic field and bone morphogenetic protein-2 expression. The
regulated the orientation of cells and bone formation results showed that the electromagnetic fields at 1.5 ~
parallel to the static magnetic field direction (Figure 2.4 mT groups significantly increased the osteoblasts
2B and 2C). Some studies have shown that magnetic differentiation and the expression of Collagen-I mRNA
nanoparticles in 3D printed scaffolds could also and bone morphogenetic protein-2. Moreover, the
pro duce magnetic stimulation on bone cells [65–67] . calcium content and calcified nodules of the 1.8 mT
Huang et al. investigated the effects of magnetic group were highest than other groups. Kamolmatyakul
stimulation which produced by incorporation of Fe O et al. [70] reported that pulse electromagnetic field (50
2
3
magnetic nanoparticle in polylactic-co-glycolic acid/ Hz, 1.5 mV/cm) significantly increased the proliferation
collagen/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds on bone rate of osteoblast-like cells. Diniz et al. [71] proposed
mesenchymal stem cells. They found that the magnetic that pulse electromagnetic field (15 Hz, 7 mT) could
nanocomposite scaffolds obviously enhanced the promote osteoblasts differentiation in the proliferation
proliferation and differentiation of bone mesenchymal and differentiation stage, and they pointed out that the
[65]
stem cells . promotion was not associated with the increased number
Pulse electromagnetic field could induce bone of cells. Wang et al. investigated the effects of 15 Hz
[72]
formation as well as inhibit bone resorption by re- pulse electromagnetic field with various intensities of
gulating the osteoblasts and osteoclasts formation, 0, 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 mT on osteoclast. The results showed
proliferation and differentiation. The effectiveness of that 0.5 mT pulse electromagnetic field significantly
regulation depended on the magnetic field intensity. inhibited the osteoclast formation and maturation. Chang
4 International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 2