Page 112 - IJB-4-2
P. 112
Shuai C, et al.
A
B
C
B1 B2 C1
C2
B3 B4
C3 C4
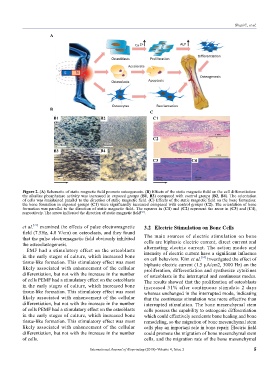
Figure 2. (A) Schematic of static magnetic field promote osteogenesis. (B) Effects of the static magnetic field on the cell differentiation:
the alkaline phosphatase activity was increased in exposed groups (B1, B3) compared with control groups (B2, B4). The orientation
of cells was maintained parallel to the direction of static magnetic field. (C) Effects of the static magnetic field on the bone formation:
the bone formation in exposed groups (C1) were significantly increased compared with control groups (C2). The orientation of bone
formation was parallel to the direction of static magnetic field. The squares in (C1) and (C2) represent the areas in (C3) and (C4),
respectively. The arrow indicated the direction of static magnetic field .
[36]
et al. [73] examined the effects of pulse electromagnetic 3.2 Electric Stimulation on Bone Cells
field (7.5Hz, 4.8 V/cm) on osteoclasts, and they found
that the pulse electromagnetic field obviously inhibited The main sources of electric stimulation on bone
the osteoclastogenesis. cells are biphasic electric current, direct current and
EMF had a stimulatory effect on the osteoblasts alternating electric current. The action modes and
in the early stages of culture, which increased bone intensity of electric current have a significant influence
on cell behaviors. Kim et al. investigated the effect of
[14]
tissue-like formation. This stimulatory effect was most biphasic electric current (1.5 μA/cm2, 3000 Hz) on the
likely associated with enhancement of the cellular proliferation, differentiation and synthesize cytokines
differentiation, but not with the increase in the number of osteoblasts in the interrupted and continuous modes.
of cells PEMF had a stimulatory effect on the osteoblasts The results showed that the proliferation of osteoblasts
in the early stages of culture, which increased bone increased 31% after continuous stimulate 2 days
tissue-like formation. This stimulatory effect was most whereas unchanged in the interrupted mode, indicating
likely associated with enhancement of the cellular that the continuous stimulation was more effective than
differentiation, but not with the increase in the number interrupted stimulation. The bone mesenchymal stem
of cells PEMF had a stimulatory effect on the osteoblasts cells possess the capability to osteogenic differentiation
in the early stages of culture, which increased bone which could effectively accelerate bone healing and bone
tissue-like formation. This stimulatory effect was most remodeling, so the migration of bone mesenchymal stem
likely associated with enhancement of the cellular cells play an important role in bone repair. Electric field
differentiation, but not with the increase in the number could promote the migration of bone mesenchymal stem
of cells. cells, and the migration rate of the bone mesenchymal
International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 2 5