Page 118 - IJB-4-2
P. 118
Shuai C, et al.
limbs. The results showed that the average trabecular bone-related diseases such as fracture, osteoporosis,
thickness, bone mineral content and bone volume bone delayed union or nonunion, etc., owing to their
fraction increased 12%, 14% and 15%, respectively. non-invasive, no infection, no side effects and ease of
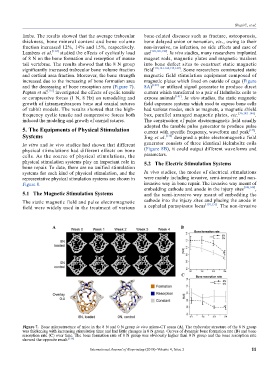
Lambers et al. [134] studied the effects of cyclically load use [120,126,138] . In vivo studies, many researchers implanted
of 8 N on the bone formation and resorption of mouse magnet rods, magnetic plates and magnetic washers
tail vertebrae. The results showed that the 8 N group into bone defect sites to construct static magnetic
significantly increased trabecular bone volume fraction field [118,121-124,139,140] . Some researchers constructed static
and cortical area fraction. Moreover, the bone strength magnetic field stimulation equipment composed of
increased due to the increasing of bone formation area magnetic plates which fixed on outside of cage (Figure
and the decreasing of bone resorption area (Figure 7). 8A) [120] or utilized signal generator to produce direct
Peptan et al. [135] investigated the effects of cyclic tensile current which transferred to a pair of Helmholtz coils to
or compressive forces (1 N, 8 Hz) on remodeling and expose animals [141] . In vitro studies, the static magnetic
growth of intramembranous bone and cranial sutures field exposure systems which used to expose bone cells
of rabbit models. The results showed that the high- had various modes, such as magnets, a magnetic shield
frequency cyclic tensile and compressive forces both box, parallel arranged magnetic plates, etc. [36,142–146] .
induced the modeling and growth of cranial sutures. The construction of pulse electromagnetic field usually
adopted the tunable pulse generator to produce pulse
5. The Equipments of Physical Stimulation current with specific frequency, waveform and peak [147] .
Systems Jing et al. [136] designed a pulse electromagnetic field
In vitro and in vivo studies had shown that different generator consists of three identical Helmholtz coils
physical stimulations had different effects on bone (Figure 8B), it could output different waveforms and
cells. As the source of physical stimulations, the parameters.
physical stimulation systems play an important role in 5.2 The Electric Stimulation Systems
bone repair. To date, there are no unified stimulation
systems for each kind of physical stimulation, and the In vivo studies, the modes of electrical stimulations
representative physical stimulation systems are shown in were mainly including invasive, semi-invasive and non-
Figure 8. invasive way in bone repair. The invasive way meant of
embedding cathode and anode in the injury sites [148,149] ,
5.1 The Magnetic Stimulation Systems and the semi-invasive way meant of embedding the
The static magnetic field and pulse electromagnetic cathode into the injury sites and placing the anode in
[150,151]
field were widely used in the treatment of various a cephalad paraspinous locus . The non-invasive
A B
C
Figure 7. Bone microstructure of mice in the 8 N and 0 N group in vivo micro-CT scans (A). The trabecular structure of the 8 N group
was thickening with increasing stimulation time and had little changes in 0 N group. Curves of dynamic bone formation rate (B) and bone
resorption rate (C) over time. The bone formation rate of 8 N group was obviously higher than 0 N group and the bone resorption rate
showed the opposite result. [134]
International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 2 11