Page 131 - IJB-4-2
P. 131
Fabrication of biomimetic placental barrier structures within a microfluidic device utilizing two-photon polymerization
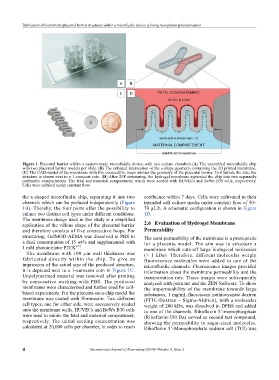
Figure 1. Placental barrier within a custom-made microfluidic device with two culture chambers.(A) The assembled microfluidic chip
with two placental barrier models per slide. (B) The enlarged intersection of the x-shape geometry containing the 3D printed membrane.
(C) The CAD-model of the membrane with five consecutive loops mimics the geometry of the placental barrier. To illustrate the size, the
structure is shown next to a 1-eurocent coin. (D) After 2PP structuring, the hydrogel membrane separated the chip into two separately
perfusable compartments. The fetal and maternal compartment, which were seeded with HUVECs and BeWo B30 cells, respectively.
Cells were cultured under constant flow.
the x-shaped microfluidic chip, separating it into two confluence within 7 days. Cells were cultivated in their
channels which can be perfused independently (Figure intended cell culture media under constant flow of 50–
1B). Thereby, the four ports offer the possibility to 70 µL/h. A schematic configuration is shown in Figure
culture two distinct cell types under different conditions. 1D.
The membrane design used in this study is a simplified
replication of the villous shape of the placental barrier 2.6 Evaluation of Hydrogel Membrane
and therefore consists of five consecutive loops. For Permeability
structuring, GelMOD-AEMA was dissolved in PBS to The semi-permeability of the membrane is a prerequisite
a final concentration of 15 wt% and supplemented with for a placenta model. The aim was to structure a
[10]
1 mM photoinitiator P2CK . membrane which cuts-off large biological molecules
The membrane with 100 µm wall thickness was (> 1 kDa). Therefore, different molecular weight
fabricated directly within the chip. To give an fluorescence molecules were added to one of the
impression of the actual size of the produced structure, microfluidic channels. Fluorescence images provided
it is depicted next to a 1-eurocent coin in Figure 1C. information about the membrane permeability and the
Unpolymerized material was removed after printing transportation rate. Those images were subsequently
by consecutive washing with PBS. The produced analyzed with paint.net and the ZEN Software. To show
membranes were characterized and further used for cell- the impermeability of the membrane towards large
based experiments. For the placenta-on-a-chip model the substances, 1 mg/mL fluorescein isothiocyanate dextran
membrane was coated with fibronectin. Two different (FITC-Dextran – Sigma-Aldrich), with a molecular
cell types, one for either side, were successively seeded weight of 200 kDa, was dissolved in DPBS and added
onto the membrane walls. HUVECs and BeWo B30 cells to one of the channels. Riboflavin 5’-monophosphate
were used to mimic the fetal and maternal compartment, (Riboflavin-350 Da) served as second test compound,
respectively. The initial seeding concentration was showing the permeability to sugar-sized molecules.
calculated at 20,000 cells per chamber, in order to reach Riboflavin 5’-Monophosphate sodium salt (TCI) was
4 International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 2