Page 38 - IJB-4-2
P. 38
Bioprinting of artificial blood vessels
in tissues engineering to allow for biofabrication This article provides a review on the different approaches
of larger tissues. Since the last decades, there had available for bioprinting of blood vessels. In this review,
been much improvements and changes to the various the term scaffold refers to the 3D material prior to cell
approaches of vascular engineering. This can be culture. The term construct is used to identify scaffolds
attributed to advancing three-dimensional (3D) printing which have undergone cell culture or are encapsulated
technologies and increasing knowledge on materials with cells.
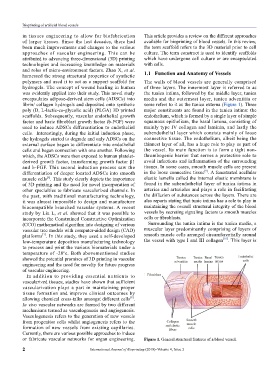
and roles of micro-environment factors. Zhao X, et al. 1.1 Function and Anatomy of vessels
harnessed the strong structural properties of synthetic
polymers and used it to act as a support scaffold for The walls of blood vessels are generally comprised
hydrogels. The concept of wound healing in human of three layers. The innermost layer is referred to as
was evidently applied into their study. This novel study the tunica intima, followed by the middle layer, tunica
encapsulates adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) into media and the outermost layer, tunica adventitia or
fibrin/ collagen hydrogels and deposited onto synthetic some refers to it as the tunica externa (Figure 1). Three
poly (D, L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) 3D printed major constituents are found in the tunica intima: the
scaffolds. Subsequently, vascular endothelial growth endothelium, which is formed by a single layer of simple
factor and basic fibroblast growth factor (b-FGF) were squamous epithelium, the basal lamina, consisting of
used to induce ADSCs differentiation to endothelial mainly type IV collagen and laminin, and lastly the
cells. Interestingly, during the initial induction phase, subendothelial layer which consists mainly of loose
the hydrogels started to degrade and only ADSCs on the connective tissue. The endothelium, albeit being the
external surface began to differentiate into endothelial thinnest layer of all, has a huge role to play as part of
cells and began connection with one another. Following the vessel. Its main function is to form a tight non-
which, the ADSCs were then exposed to human platelet- thrombogenic barrier that serves a protective role to
derived growth factor, transforming growth factor β1 avoid infections and inflammation of the surrounding
and b-FGF. This second induction process saw the tissues. In some cases, smooth muscle cells are present
[9]
differentiation of deeper located ADSCs into smooth in the loose connective tissue . A fenestrated acellular
[6]
muscle cells . This study clearly depicts the importance elastic lamella called the internal elastic membrane is
of 3D printing and the need for novel incorporation of found in the subendothelial layer of tunica intima in
other specialties to fabricate vascularized channels. In arteries and arterioles and plays a role in facilitating
the past, with traditional manufacturing technology, the diffusion of substances across the layers. There are
it was almost impossible to design and manufacture also reports stating that tunic intima has a role to play in
biocompatible branched vascular systems. A recent maintaining the overall structural integrity of the blood
study by Liu L, et al. showed that it was possible to vessels by secreting signaling factors to smooth muscles
incorporate the Constrained Constructive Optimization cells or fibroblasts.
(CCO) mathematical algorithm into designing of various Surrounding the tunica intima is the tunica media, a
vascular tree models with computer-aided design (CAD) muscular layer predominantly comprising of layers of
[7]
platforms . In this study, they used a self-developed smooth muscle cells arranged circumferentially around
[10]
low-temperature deposition manufacturing technology the vessel with type I and III collagen . This layer is
to process and print the various biomaterials under a
temperature of -20ºc. Both abovementioned studies
showed the potential promises of 3D printing in vascular
engineering and the need for novelty for future progress
of vascular engineering.
In addition to providing essential nutrients to
vascularized tissues, studies have shown that sufficient
vascularization plays a part in maintaining proper
tissue formation and improve clinical outcomes by
[8]
allowing chemical cross-talks amongst different cells .
In vivo vascular networks are formed by two different
mechanisms termed as vasculogenesis and angiogenesis.
Vasculogenesis refers to the generation of new vessels
from progenitor cells whilst angiogenesis refers to the
formation of new vessels from existing capillaries.
Currently, there are various possible approaches to induce
or fabricate vascular networks for organ engineering. Figure 1. General structural features of a blood vessel.
2 International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 2