Page 256 - IJB-10-4
P. 256
International Journal of Bioprinting Cell viability in printing structured inks
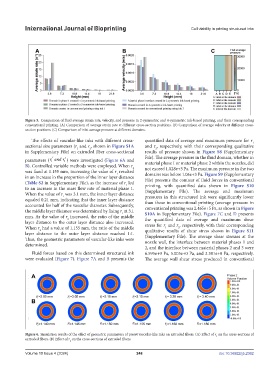
Figure 5. Comparison of fluid average strain rate, velocity, and pressure in 2-symmetric and 4-symmetric ink-based printing, and their corresponding
conventional printing. (A) Comparison of average strain rate at different cross-section positions. (B) Comparison of average velocity at different cross-
section positions. (C) Comparison of inlet average pressure at different domains.
The effects of vascular-like inks with different cross- quantified data of average and maximum pressure for r
1
sectional size parameters (r and r , shown in Figure S1A and r , respectively, with their corresponding qualitative
2
2
1
in Supplementary File) on extruded fiber cross-sectional results of pressure shown in Figure S8 (Supplementary
′
parameters ( rand r′ File). The average pressure in the fluid domain, whether in
2 ) were investigated (Figure 6A and
1
B). Controlled variable methods were employed. When r 2 material phase 1 or material phase 2 within the nozzles, did
not exceed 1.028e+3 Pa. The maximum pressure in the two
was fixed at 1.155 mm, increasing the value of r resulted domains was below 1.06e+3 Pa. Figure S9 (Supplementary
1
in an increase in the proportion of the inner layer distance File) presents the contour of fluid forces in conventional
(Table S2 in Supplementary File), as the increase of r led printing, with quantified data shown in Figure S10
1
to an increase in the mass flow rate of material phase 1. (Supplementary File). The average and maximum
When the value of r was 3.1 mm, the inner layer distance pressures in this structured ink were significantly lower
1
equaled 0.21 mm, indicating that the inner layer distance than those in conventional printing (average pressure in
accounted for half of the vascular diameter. Subsequently, conventional printing was 2.465e+5 Pa, as shown in Figure
the middle layer distance was determined by fixing r at 3.1 S10A in Supplementary File). Figure 7C and D presents
1
mm. As the value of r increased, the ratio of the middle the quantified data of average and maximum shear
2
layer distance to the outer layer distance also increased. stress for r and r , respectively, with their corresponding
When r had a value of 1.155 mm, the ratio of the middle qualitative results of shear stress shown in Figure S11
2
1
2
layer distance to the outer layer distance reached 1:1. (Supplementary File). The average shear stresses at the
Thus, the geometric parameters of vascular-like inks were nozzle wall, the interface between material phases 1 and
determined.
2, and the interface between material phases 2 and 3 were
Fluid forces based on this determined structured ink 6.595e+0 Pa, 5.005e+0 Pa, and 3.381e+0 Pa, respectively.
were evaluated (Figure 7). Figure 7A and B presents the The average wall shear stress produced in conventional
Figure 6. Simulation results of the effect of geometric parameters of preset vascular-like inks on extruded fibers. (A) Effect of r on the cross-sections of
1
extruded fibers. (B) Effect of r on the cross-sections of extruded fibers.
2
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 248 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2362