Page 259 - IJB-10-4
P. 259
International Journal of Bioprinting Cell viability in printing structured inks
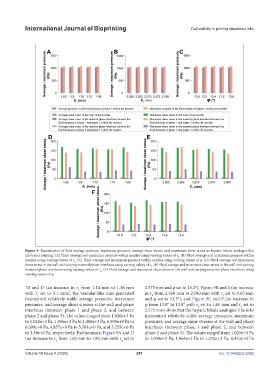
Figure 9. Examination of fluid average pressure, maximum pressure, average shear stress, and maximum shear stress in hepatic lobule analogue-like
ink-based printing. (A) Fluid average and maximum pressure within nozzles using varying values of r . (B) Fluid average and maximum pressure within
3
nozzles using varying values of r . (C) Fluid average and maximum pressure within nozzles using varying values of φ. (D) Fluid average and maximum
4
shear stress in the wall and varying material phase interfaces using varying values of r . (E) Fluid average and maximum shear stress in the wall and varying
3
material phase interfaces using varying values of r . (F) Fluid average and maximum shear stress in the wall and varying material phase interfaces using
4
varying values of φ.
7B and D (an increase in r from 1.14 mm to 1.16 mm 2.575 mm and φ set to 13.3°), Figure 9B and E (an increase
2
with r set to 3.1 mm), the vascular-like inks generated in r from 2.560 mm to 2.580 mm with r set to 1.65 mm
1
3
4
maintained relatively stable average pressures, maximum and φ set to 13.3°), and Figure 9C and F (an increase in
pressures, and average shear stresses at the wall and phase φ from 13.0° to 13.8° with r set to 1.65 mm and r set to
4
3
interfaces (between phase 1 and phase 2, and between 2.575 mm) show that the hepatic lobule analogue-like inks
phase 2 and phase 3). The values ranged from 1.026e+3 Pa maintained relatively stable average pressures, maximum
to 1.028e+3 Pa, 1.056e+3 Pa to 1.060e+3 Pa, 6.595e+0 Pa to pressures, and average shear stresses at the wall and phase
6.600e+0 Pa, 4.837e+0 Pa to 5.181e+0 Pa, and 3.255e+0 Pa interfaces (between phase 1 and phase 2, and between
to 3.38e+0 Pa, respectively. Furthermore, Figure 9A and D phase 2 and phase 3). The values ranged from 1.025e+3 Pa
(an increase in r from 1.60 mm to 1.80 mm with r set to to 1.030e+3 Pa, 1.064e+3 Pa to 1.070e+3 Pa, 6.410e+0 Pa
3 4
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 251 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2362