Page 266 - IJB-10-4
P. 266
International Journal of Bioprinting Cell viability in printing structured inks
Furthermore, as the structured inks are extruded in the outer layer of the ink and in intermediary and outer
and deposited onto the printing platform, the velocity layers, respectively.
decreases from a certain value to 0. The printing 18G needles were involved. Following the printing of
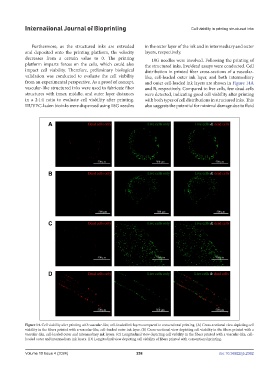
platform imparts forces on the cells, which could also the structured inks, live/dead assays were conducted. Cell
impact cell viability. Therefore, preliminary biological distribution in printed fiber cross-sections of a vascular-
validation was conducted to evaluate the cell viability like, cell-loaded outer ink layer, and both intermediary
from an experimental perspective. As a proof of concept, and outer cell-loaded ink layers are shown in Figure 14A
vascular-like structured inks were used to fabricate fiber and B, respectively. Compared to live cells, few dead cells
structures with inner, middle, and outer layer distances were detected, indicating good cell viability after printing
in a 2:1:1 ratio to evaluate cell viability after printing. with both types of cell distributions in structured inks. This
HUVEC-laden bioinks were dispensed using 18G needles also suggests the potential for minimal damage due to fluid
Figure 14. Cell viability after printing with vascular-like, cell-loaded ink layers compared to conventional printing. (A) Cross-sectional view depicting cell
viability in the fibers printed with a vascular-like, cell-loaded outer ink layer. (B) Cross-sectional view depicting cell viability in the fibers printed with a
vascular-like, cell-loaded outer and intermediary ink layers. (C) Longitudinal view depicting cell viability in the fibers printed with a vascular-like, cell-
loaded outer and intermediary ink layers. (D) Longitudinal view depicting cell viability of fibers printed with conventional printing.
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 258 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2362