Page 99 - IJB-5-2
P. 99
Fang A, et al.
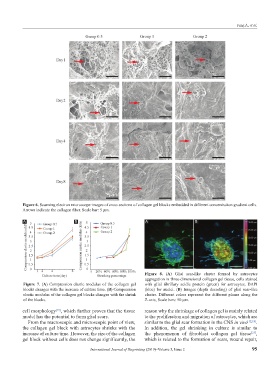
Figure 6. Scanning electron microscope images of cross sections of collagen gel blocks embedded in different concentration gradient cells.
Arrows indicate the collagen fiber. Scale bar: 5 μm.
A B A B
Figure 8. (A) Glial scar-like cluster formed by astrocytes
aggregation in three-dimensional collagen gel tissue, cells stained
Figure 7. (A) Compression elastic modulus of the collagen gel with glial fibrillary acidic protein (green) for astrocytes, DAPI
blocks changes with the increase of culture time. (B) Compression (blue) for nuclei. (B) Images (depth decoding) of glial scar-like
elastic modulus of the collagen gel blocks changes with the shrink cluster. Different colors represent the different planes along the
of the blocks. Z-axis, Scale bars: 50 μm.
cell morphology [19] , which further proves that the tissue reason why the shrinkage of collagen gel is mainly related
model has the potential to form glial scars. to the proliferation and migration of astrocytes, which are
From the macroscopic and microscopic point of view, similar to the glial scar formation in the CNS in vivo [12,18] .
the collagen gel block with astrocytes shrinks with the In addition, the gel shrinking in culture is similar to
increase of culture time. However, the size of the collagen the phenomenon of fibroblast collagen gel tissue ,
[25]
gel block without cells does not change significantly, the which is related to the formation of scars, wound repair,
International Journal of Bioprinting (2019)–Volume 5, Issue 2 95