Page 138 - IJB-10-5
P. 138
International Journal of Bioprinting Liver printing: from structure to application
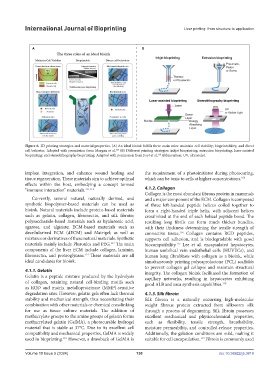
Figure 6. 3D printing strategies and material properties. (A) An ideal bioink fulfills three main roles: maintain cell viability; bioprintability; and direct
104
cell behavior. Adapted with permission from Morgan et al. (B) Different printing strategies: inkjet bioprinting; extrusion bioprinting; laser-assisted
148
bioprinting; and stereolithography bioprinting. Adapted with permission from Foyt et al. Abbreviation: UV, ultraviolet.
implant integration, and enhance wound healing and the requirement of a photoinitiator during photocuring,
tissue regeneration. These materials aim to achieve optimal which can be toxic to cells at higher concentrations. 106
effects within the host, embodying a concept termed
“immune interaction” materials. 111,112 4.1.2. Collagen
Collagen is the most abundant fibrous protein in mammals
Currently, several natural, naturally derived, and and a major component of the ECM. Collagen is composed
synthetic biopolymer-based materials can be used as of three left-handed peptide helices coiled together to
bioink. Natural materials include protein-based materials form a right-handed triple helix, with adjacent helices
such as gelatin, collagen, fibronectin, and silk fibroin; crosslinked at the end of each helical peptide bond. The
polysaccharide-based materials such as hyaluronic acid, resulting long fibrils can form much thicker bundles,
agarose, and alginate; ECM-based materials such as with their thickness determining the tensile strength of
decellularized ECM (dECM) and Matrigel; as well as connective tissue. Collagen contains RGD peptides,
116
mixtures or derivatives of these natural materials. Synthetic supports cell adhesion, and is biodegradable with good
materials mainly include Pluronics and PEG. The main biocompatibility. Lee et al. encapsulated hepatocytes,
113
117
components of the liver ECM include collagen, laminin, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), and
fibronectin, and proteoglycans. These materials are all human lung fibroblasts with collagen as a bioink, while
114
ideal candidates for bioink. simultaneously printing polycaprolactone (PCL) scaffolds
to prevent collagen gel collapse and maintain structural
4.1.1. Gelatin integrity. The collagen bioink facilitated the formation of
Gelatin is a peptide mixture produced by the hydrolysis capillary networks, resulting in hepatocytes exhibiting
of collagen, retaining natural cell-binding motifs such good ALB and urea synthesis capabilities. 118
as RGD and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-sensitive
degradation sites. However, gelatin gels often lack thermal 4.1.3. Silk fibroin
stability and mechanical strength, thus necessitating their Silk fibroin is a naturally occurring high-molecular
combination with other materials or chemical crosslinking weight fibrous protein extracted from silkworm silk
for use as tissue culture materials. The addition of through a process of degumming. Silk fibroin possesses
methacrylate groups to the amine groups of gelatin forms excellent mechanical and physicochemical properties,
methacrylated gelatin (GelMA), a photocurable hydrogel such as flexibility, tensile strength, breathability,
material that is stable at 37°C. Due to its excellent cell moisture permeability, and controlled-release properties.
compatibility and mechanical properties, GelMA is widely Additionally, the gelation conditions are mild, making it
used in bioprinting. However, a drawback of GelMA is suitable for cell encapsulation. Fibroin is commonly used
115
119
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 130 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3819