Page 255 - IJB-10-5
P. 255
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed hydrogels for tumor therapy
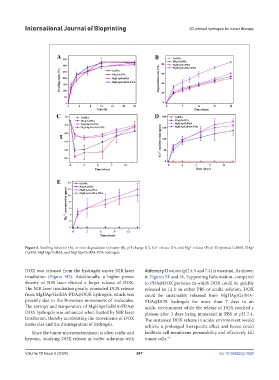
Figure 8. Swelling behavior (A), in vitro degradation behavior (B), pH change (C), Ca release (D), and Mg release (E) of 3D-printed GelMA, HAp/
2+
2+
GelMA, MgHAp/GelMA, and MgHAp/GelMA-PDA hydrogels.
DOX was released from the hydrogels under NIR laser different pH values (pH 4.5 and 7.4) is essential. As shown
irradiation (Figure 9D). Additionally, a higher power in Figures 9E and S6, Supporting Information, compared
density of NIR laser elicited a larger release of DOX. to PDA@DOX particles in which DOX could be quickly
The NIR laser irradiation greatly promoted DOX release released in 12 h in either PBS or acidic solution, DOX
from MgHAp/GelMA-PDA@DOX hydrogels, which was could be sustainably released from MgHAp/GelMA-
possibly due to the Brownian movements of molecules. PDA@DOX hydrogels for more than 7 days in an
The entropy and temperature of MgHAp/GelMA-PDA@ acidic environment while the release of DOX reached a
DOX hydrogels was enhanced when heated by NIR laser plateau after 3 days being immersed in PBS at pH 7.4.
irradiation, thereby accelerating the movements of DOX The sustained DOX release in acidic environment would
molecules and the disintegration of hydrogels. achieve a prolonged therapeutic effect and hence could
Since the tumor microenvironment is often acidic and facilitate cell membrane permeability and effectively kill
hypoxic, studying DOX release in buffer solutions with tumor cells.
64
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 247 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3526