Page 50 - IJB-6-1
P. 50
HRP plus glucose-mediated bioprinting
D-glucose (44 mg/mL), and CNF (1.5 w/v%) using a fluorescence microscope (BZ-9000,
at 5 × 10 cells/mL, as a bioink. The cell-laden Keyence Corp., Osaka, Japan).
5
lattice-shaped constructs were printed in a safety
cabinet and kept in an incubator until the complete 2.6 Switching hydrogel surface
cross-linking. As a non-printed hydrogel, the Lattice-shaped hydrogel construct was printed
mixture solution was poured into 24-well plate first using the selected ink on a culture dish with
at 0.25 mL/well. The resultant hydrogels were a surface covered with 1.0% agarose gel. After
incubated in DMEM at 37°C. After 1 day and post-cross-linking, the hydrogel construct was
7 days of incubation, the cells in hydrogels soaked in a solution containing Rho-Gel-Ph
were stained with Calcein-AM (live cells) and (1.0 w/v%) for overnight at 37°C. Then, the
propidium iodide (dead cells) for the observation construct was rinsed well with PBS to remove
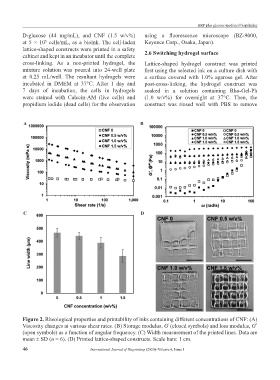
A B
C D
Figure 2. Rheological properties and printability of inks containing different concentrations of CNF: (A)
Viscosity changes at various shear rates. (B) Storage modulus, G (closed symbols) and loss modulus, G
ʹ
ʹʹ
(open symbols) as a function of angular frequency. (C) Width measurement of the printed lines. Data are
mean ± SD (n = 6). (D) Printed lattice-shaped constructs. Scale bars: 1 cm.
46 International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 1