Page 62 - IJB-6-2
P. 62
Effects of topology optimization in multimaterial 3D bioprinting of soft actuators
A to once side of the actuator decreased leading to
a slower rate of swelling and as a consequence
smaller bending index.
The electroactivity of the 3D-printed
polyelectrolyte actuator increased as the DC
voltage increased. Yet, at higher voltages of
more than 10 V, the electrochemical reactions
intensify leading to significant acceleration
of the electrochemically generated ion waves
and electrolysis bubbles in the cell. These
B circumstances require further computational fluid
dynamics analysis to be incorporated into the TO
algorithm, which is beyond the scope of our study.
The 3D-printed bioactuator developed
here is used as an ad hoc to demonstrate the
capability of TO for functionality enhancement.
The contribution of the TO may be influenced
by optimization of synthesis parameters to
improve the overall electro-chemo-mechanical
performance of the actuator. In other words, the
bending amplitude of such actuators could be
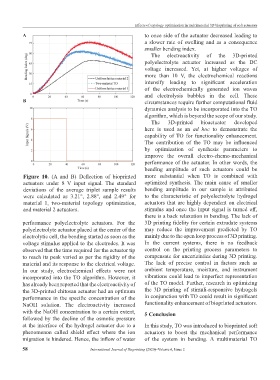
Figure 10. (A and B) Deflection of bioprinted more substantial when TO is combined with
actuators under 8 V input signal. The standard optimized synthesis. The main cause of smaller
deviations of the average triplet sample results bending amplitude in our sample is attributed
were calculated as 3.21°, 2.88°, and 2.49° for to the characteristic of polyelectrolyte hydrogel
material 1, two-material topology optimization, actuators that are highly dependent on electrical
and material 2 actuators. stimulus and once the input signal is turned off,
there is a back relaxation in bending. The lack of
performance polyelectrolyte actuators. For the 3D printing fidelity for certain extrudate systems
polyelectrolyte actuator placed at the center of the may reduce the improvement predicted by TO
electrolytic cell, the bending started as soon as the mainly due to the open loop process of 3D printing.
voltage stimulus applied to the electrodes. It was In the current systems, there is no feedback
observed that the time required for the actuator tip control on the printing process parameters to
to reach its peak varied as per the rigidity of the compensate for uncertainties during 3D printing.
material and its response to the electrical voltage. The lack of precise control in factors such as
In our study, electrochemical effects were not ambient temperature, moisture, and instrument
incorporated into the TO algorithm. However, it vibrations could lead to imperfect representation
has already been reported that the electroactivity of of the TO model. Further, research in optimizing
the 3D-printed chitosan actuator had an optimum the 3D printing of stimuli-responsive hydrogels
performance in the specific concentration of the in conjunction with TO could result in significant
NaOH solution. The electroactivity increased functionality enhancement of bioprinted actuators.
with the NaOH concentration to a certain extent, 5 Conclusion
followed by the decline of the osmotic pressure
at the interface of the hydrogel actuator due to a In this study, TO was introduced to bioprinted soft
phenomenon called shield effect where the ion actuators to boost the mechanical performance
migration is hindered. Hence, the inflow of water of the system in bending. A multimaterial TO
58 International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 2