Page 46 - IJB-6-3
P. 46
Software for bioprinting
cell types). The ability of stem cells to produce
a large number of cells is the second reason for
using them [27,28] . Scaffold-based 3D models can be
generated by seeding cells or embedding cells in
a hydrogel matrix or on a prefabricated scaffold.
Widely used materials for scaffolds include
decellularized extracellular matrix components
and many synthetic and natural biomaterials.
Bioprinting technologies can be potentially useful
for the fabrication of a wide variety of tissues such
as composite tissues, vascular tissues, lung, neural,
pancreas, brain, bone, cancer, cardiac, cartilage,
heart valve, liver, retinal, skin, and others [1-5,7,8,15,25] .
In addition, there are different goals of using
bioprinting in pharmaceutical researches such
as developing drugs against cancer and other
diseases [13-17] .
Vascularization in 3D printed tissues is
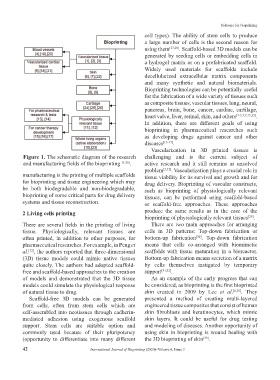
Figure 1. The schematic diagram of the research challenging and is the current subject of
and manufacturing fields of the bioprinting [1-26] . active research and it still remains as unsolved
problem [3,12] . Vascularization plays a crucial role in
manufacturing is the printing of multiple scaffolds tissue viability for its survival and growth and for
for bioprinting and tissue engineering which may drug delivery. Bioprinting of vascular constructs,
be both biodegradable and non-biodegradable, such as bioprinting of physiologically relevant
bioprinting of some critical parts for drug delivery tissues, can be performed using scaffold-based
systems and tissue reconstruction. or scaffold-free approaches. These approaches
2 Living cells printing produce the same results as in the case of the
bioprinting of physiologically relevant tissues .
[29]
There are several fields in the printing of living There are two main approaches for arranging
tissue. Physiologically, relevant tissues are cells in 3D patterns: Top-down fabrication or
often printed, in addition to other purposes, for bottom-up fabrication . Top-down fabrication
[30]
pharmaceutical researches. For example, in Peng et means that cells co-arranged with biomimetic
al. , the authors reported that three-dimensional scaffolds with tissue maturation in a bioreactor.
[12]
(3D) tissue models could mimic native tissues Bottom-up fabrication means secretion of a matrix
quite closely. The authors had adopted scaffold- by cells themselves instigated by temporary
free and scaffold-based approaches to the creation support [31,32] .
of models and demonstrated that the 3D tissue As an example of the early progress that can
models could simulate the physiological response be considered, as bioprinting is the first bioprinted
of natural tissue to drug. skin created in 2009 by Lee et al. [6,30] . They
Scaffold-free 3D models can be generated presented a method of creating multi-layered
from cells, often from stem cells which are engineered tissue composites that consist of human
self-assembled into neotissues through cadherin- skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes, which mimic
mediated adhesion using exogenous scaffold skin layers. It could be useful for drug testing
support. Stem cells are suitable option and and modeling of diseases. Another opportunity of
commonly used because of their pluripotency using skin in bioprinting is wound healing with
(opportunity to differentiate into many different the 3D bioprinting of skin .
[33]
42 International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 3