Page 11 - IJB-6-4
P. 11
He, et al.
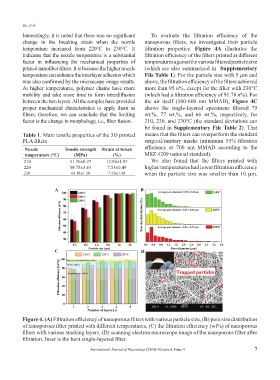
Interestingly, it is noted that there was no significant To evaluate the filtration efficiency of the
change in the breaking strain when the nozzle nanoporous filters, we investigated their particle
temperature increased from 220°C to 230°C. It filtration properties. Figure 4A illustrates the
indicates that the nozzle temperature is a substantial filtration efficiency of the filters printed at different
factor in influencing the mechanical properties of temperatures against the various filtered particle size
printed nanofiber filters. It is because the higher nozzle (which are also summarized in Supplementary
temperature can enhance the interlayer adhesion which File Table 1). For the particle size with 5 μm and
was also confirmed by the microscope image results. above, the filtration efficiency of the filters achieved
At higher temperatures, polymer chains have more more than 95 n%, except for the filter with 230°C
mobility and take more time to form interdiffusion (which had a filtration efficiency of 91.78 n%). For
between the two layers. All the samples have provided the air itself (500-600 nm MMAD), Figure 4C
proper mechanical characteristics to apply them as shows the single-layered specimens filtered 79
filters; therefore, we can conclude that the limiting wt.%, 77 wt.%, and 66 wt.%, respectively, for
factor is the change in morphology, i.e., fiber fusion. 210, 220, and 230°C (the standard deviations can
be found in Supplementary File Table 2). That
Table 1. Main tensile properties of the 3D printed means that the filters can overperform the standard
PLA filters surgical/sanitary masks (minimum 55% filtration
Nozzle Tensile strength Strain at break efficiency at 700 nm MMAD according to the
temperature (°C) (MPa) (%) MSZ 4209 national standard).
210 51.76±0.27 12.88±1.97 We also found that the filters printed with
220 58.75±3.63 7.53±0.49 higher temperatures had lower filtration efficiency
230 60.18±1.20 7.63±1.08 when the particle size was smaller than 10 μm.
A B
C D
Figure 4. (A) Filtration efficiency of nanoporous filters with various particle size, (B) pore size distribution
of nanoporous filter printed with different temperatures, (C) the filtration efficiency (wt%) of nanoporous
filters with various stacking layers, (D) scanning electron microscope image of the nanoporous filter after
filtration. Inset is the bent single-layered filter.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 4 7